Chapter-1 Indus Valley Civilization
1) In how much area was
Indus Civilization spread?
13 Lac Square Kilometer
2) In how many parts
were Indus Valley towns divided?
2 (Citadel and Lower Town)
3) Which Indus Valley
town was divided into three parts?
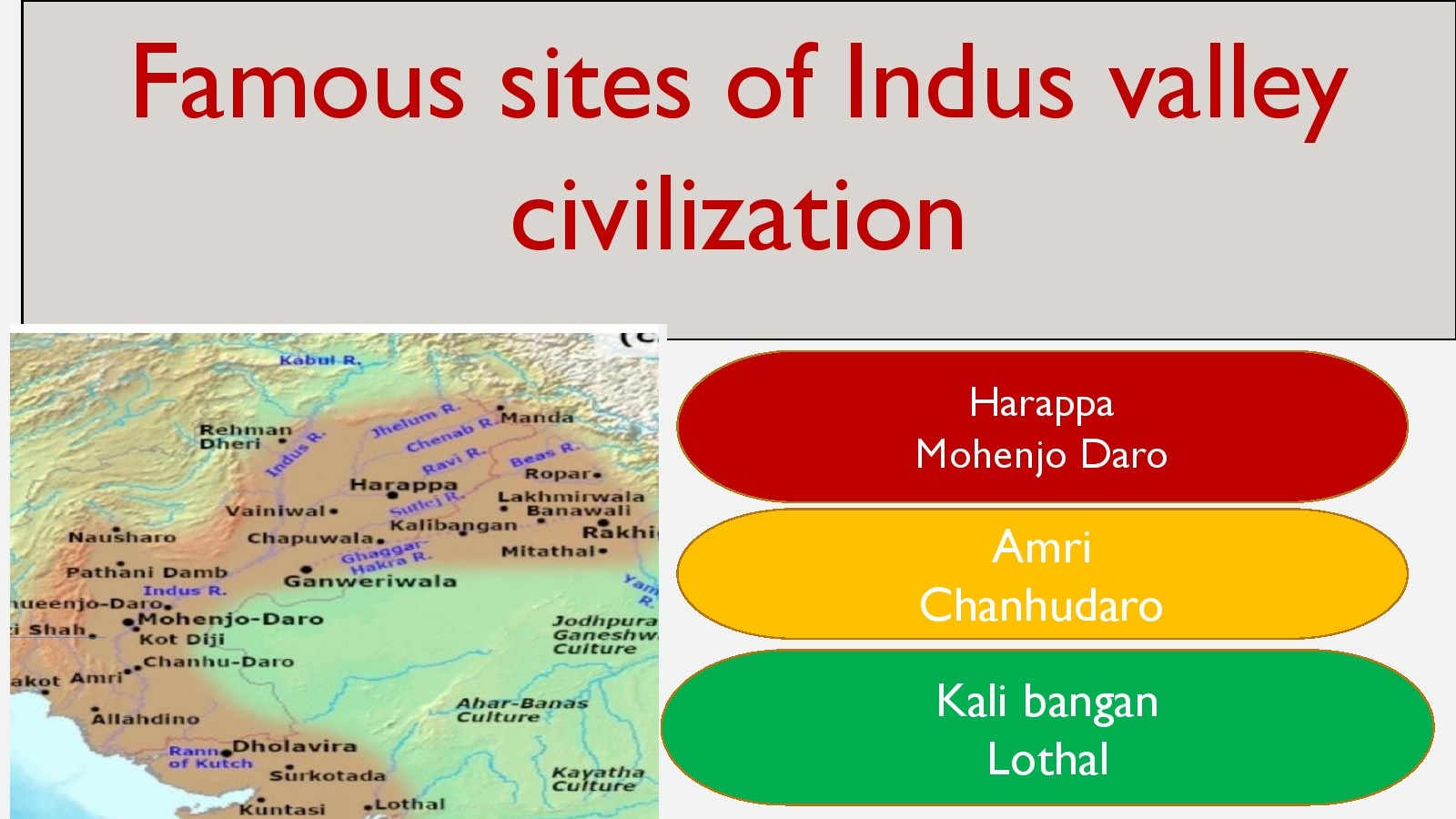
Dholavira
4) Who discovered Indus
Valley Civilization?
Daya Ram Sahni
5) Which was the first
known site of Indus Civilization?
Harappa
6) When was Harappa
discovered?
In 1921 AD
7) What is the another
name of Indus Civilization?
Harappan Civilization
8) To which age did
Indus Civilization belong?
Bronze Age
9) Which was the second
excavated site of Indus Civilization?
Mohanjodaro
10) What is meant by
Mohanjodaro?
Mound of the dead
11) How many layers of
Mohanjodaro have been discovered?
7
12) Who excavated
Mohanjodaro?
R. D. Benarjee
13) When was
Mohanjodaro excavated?
1922 AD
14) What is the most
accepted period of Indus Civilization?
2250BC-1750BC
15) How old is Indus
Civilization?
Approx. 5000 years
16) On the bank of
which river is Harappa located?
Ravi
17) Which is largest of
all Indus sites?
Harappa
18) Hown many times was
Mohanjodaro destroyed?
7 times
19) Which articles have
been found from Mohanjodaro?
Great bath, dancing girl scrupture, granery
and seals
20) Write the
dimensions of the Great Bath?
180 feet X 108 feet
21) Write the
dimenstions of pond situated in Greatbath?
39 feet X 23 feet X 7feet
22) Who excavated
Chanhudro?
N. G. Majumdar
23) When was Chanhudro
excavated?
1931 AD
24) How many times was
Chanhudro destroyed?
Twice
25) Why was Chanhudro
famous?
For beads making
26) Where is Kali
Bangan located?
Dist. Hanumangarh in Rajasthan
27) What was Kali
Bangan famous for?
Manufacturing of Black Bangles
28) When was Kali
Bangan excavated?
1953
29) Where is Lothal
located?
In Gujrat
30) Why was Lothal
famous?
For its large Dockyard
31) Where is Sanghol
located?
Dist. Fatehgarh Sahib in Punjab
32) What was the
breadth of roads in Indus Civilization?
13 feet to 34 feet
33) What were the
weapons of Indus Peaople?
Small swords, spear, arrow, axe,
knife etc.
34) What were the
weapons of Indus people made up of?
Bronze or Copper
35) What was the main
occupation of Indus people?
Agriculture
36) What were the tools
of Indus people made up of?
Wood
37) What were the main
crops of Indus people?
Wheat and Barley
38) What other crops
were grown by Indus people apart from wheat and barley?
Rice, Coconut, Date, Vegetables,
Cotton, etc.
39) For which crop
Indus Valley was famous over the world?
Cotton
40) Name the animals
reared by Indus people?
Elephant, camel, pig, sheep, dog, goat,
etc.
41) Name the countries
with whom Indus people had trade relations?
Roman, Sumarian, Mosopotamians etc.
42) Which diety was
worshipped most by Indus People?
Mother Goddess
43) What did Mother
Goddess symbolise?
Power
44) Name another God
worshipped most by Indus people after Mother Goddess.
Shiva Pashupati
45) Name some animals
worshipped by Indus People.
Elephant, Rhinocores, Tigert etc.
46) Which tree was
worshipped by Indus people?
Pipal Tree
47) What kind of
society do Indus people have?
Matriarchal Society
48) What kind of script
did Indus people use?
Pictographic
49) How many alphabets
of Indus script are found so far?
Approx. 270
50) How many Indus
Valley sites have been found so far?
More than 300 sites
51) The statue of
Priest found at Mohanjodaro is made up of which element?
White stone
52) What were the most
of Indus sculptures made up of?
Terracota
(3 Marks Questions/ Answers)
1. Mention the main
features of the town planning of Indus Valley Civilization.
Ans: Main
features:
I. Towns were well planned.
II. Houses were airy and spacious.
III. | Drains were covered.
IV. Roads cut each other on 90 degree
angle.
2. Write a short note
on Harappa.
Ans: Harappa was situated in
Mointgumari district of Punjab in present Pakistan. It was situated on the bank
of river Ravi. It was discovered by Daya Ram Sahni in 1921 AD. It is the largest
town of Indus Valley Civilization. The town was surrounded by a high wall to
protect it from enemies.
3. What do you know
about Mohanjodaro?
Ans: Mohandodaro was the second most
important town of Indus Valley Civilization. It was situated on the bank of
river Sind. It was discovered by R. D. Bannerjee in 1922 AD. Mohanjodaro
literally means ‘the Mound of the Dead’. A great bath, bronze image of dancing
girl, warehouses and a large number of coins have been found on this site.
4. Write short note on
Kalibangan.
Ans: This site is situated in Hanumangarh
district of Rajasthan. The town got its name from black bangles. This town was
discovered by A. Ghosh in 1953 AD. Traces of ploughed fields, utencils,
ornaments and toys have been found on this site.
5. Write short note on
the Great Bath.
Ans: The Great Bath has been found in
Mohanjodaro. Its length and breadth are 180 feet and 108 feet respectively. A
pond of dimensions 39 feet X 23 feet X 8 feet was constructed in the middle of
the great bath. There were stairs to get down in pond. There was a provision of
changing rooms around the Great Bath.
6. Write short note on
drainage system of Indus Valley Civilization.
Ans:
I. Drains were constructed in
scientific manner.
II. The drains from the houses flowed
into the drains into streets which further flowed into big drains.
III. Drains were covered with
removable bricks.
IV. Nobody was allowed to throw the
garbage into the drains.
7. Write the main
features of Indus Valley Houses.
Ans:
I. Houses were made of burnt bricks.
ll. | Houses had strong and deep
foundations.
III. | Houses had big doors, windows
and ventilators.
IV. Some houses had two or more
storeys.
V. Each house had an open courtyard,
a kitchen, a well and a bathroom.
8. Write short note on
technology of Indus Valley People.
Ans:
I. Indus Valley People were
technologically advanced.
II. They were experts in making
copper and bronze utencils, images, toys etc.
III. The art of making ornaments was
also highly developed.
IV. They were also skilled in making
seals, weaving cotton and woolen clothes.
9. What kind of
ornament/ jewelry did Indus People wear?
Ans:
I. Man and women, both wore
ornaments.
II Men wore necklaces, rings and
bangles.
III. Women wore necklaces, rings,
bangles, nose pins, ear rings etc.
IV. Ornaments were made up of gold,
silver, ivory and precious stones.
V. Poor people wore ornaments made of
copper.
10. How did the people
of Indus Valley Civilization entertain themselves?
Ans:
I. The people of Indus Valley
entertained themselves by a variety of sources.
II. They were fond of playing chess,
hunting, watching animal’s fights, of music and dance.
III. Children entertained themselves
by toys.
11. What do you know
about the dress of Indus Valley People?
Ans:
I Indus people wore cotton and woolen
clothes.
II. Male covered they body with cloth
sheet known as chadar or dhoti.
III. Women wore lehanga and choli.
IV. They knew the art of stitching.
12. How did the Indus
People dispose the dead?
Ans: They
disposed the dead bodies in three ways:
I. The dead were cremated and their
ashes were buried in the ground.
II. Sometimes the body itself was
buried in the ground.
III. At other times, they throw the
dead body in some open place and later buried only the skeleton.
13. What do you know
about the foreign trade of Indus people?
Ans:
I. Indus people had trade relations
with Sumerians, Mesopotamians and Egyptians.
II. They imported gold, silver,
cosmetics and precious stones.
III. They exported cotton clothes,
ornaments, ivory, beads, monkeys, peacocks etc.
IV. Harappa, Mohenjo-Daro and Lothal
were famous trade centers.
14. What were the
characteristics of religion of Indus Valley people?
Ans:
I. People mainly used to worship
Mother Goddess.
II. They also worshipped Lord Shiva.
III. Besides theses, they also
worshipped Linga, Yoni, Sun, Ox, Tiger and Elephants etc.
IV. They believed in magic and
charms.
15. What type of seals
has been found in Indus Valley Civilization?
Ans:
I. A large number of seals have been
found from Indus Valley Civilization.
II. More than 1200 seals have been
found only at Mohanjo-daro.
Ill. These were made of baked clay,
lime and ivory.
IV. These seals contain the figures
of humans, animals and trees.
16. Write short note on
polity in Indus Valley Civilization.
Ans:
I. There are different opinions among
historians about the political life of Indus people.
II. The uniform town planning, seals,
weights and measures depict that their political system was good and stable.
III. The facilities available in Indus
towns show that there must have been municipalities.
17. Write short note on
the script of Indus Valley people.
Ans:
I. The script of Indus people was
pictographic.
II. Around 270 symbol have been found
of their script.
III. These symbols have been found on
seals, strips, pots and walls.
IV. The script was written from left
to right.
V. The script has not been deciphered
still.
18. Write short note on
Art of Indus Valley people.
Ans:
I. Indus people made a lot of
progress in the field of art.
II. They were adept in making
sculpture of idols, stone and terracotta.
III. They liked drawing and painting.
IV. Bronze figure of dancing girl is
the best example their artistic skill.
19. Give a brief
account of legacy of Indus Valley Civilization.
Ans:
I. The Indus Valley Civilization has
left deep impression on Indian culture and civilization.
II. We have learnt the art of town
planning, wide roads, lighting arrangement etc. from Indus Valley people.
III. Art of making toys, cosmetic,
spindle etc. were learnt from this civilization.
IV. The religious faith practiced in
Indus Valley civilization are still the part of Hinduism.
20. What were the
causes of decline and disappearance of Indus Valley Civilization?
Ans: According to different
historians, following are the possible causes of decline of Indus Valley
Civilization:
I. The invasions of Aryans.
II. Frequent floods.
III. Frequent earthquakes.
IV. Climate change
V. Some epidemic i.e. plague or
malaria etc.
VI. The Indus river has changed it course
that led to draught in area.
Long Answer types questions (6 marks)
Question: -1 What are the centers of
Indus Valley Civilization found in modern Pakistan and India?
Answer: The history of India is
believed to have started from the Indus Valley, the oldest civilization of
India. About 5000 years old Indus civilization has found 300 centers in modern Pakistan
and India. The
main centers and their features are described as follows: -
|
Sr.no |
Location |
Country |
Invention
year |
Famous
for |
|
1. |
Harapan |
Pakistan |
1921
A.D |
Well
planned Towns |
|
2. |
Mohenjo-Daro |
Pakistan |
1922
A.D |
The
great Bathroom Trade centre |
|
3. |
Chanhudro |
Pakistan |
1931
A.D |
Beads,
Famous for copper and Bronze tools cane For tools |
|
4. |
Kotla
Nihang Khan (Ropar) |
India
(Punjab) |
1953
A.D |
Utensils,
Jewellery Tools |
|
5. |
Kali
Bangan(Ganga Nagar) |
India
(Rajasthan) |
1953
A.D |
Black
bangles Well planned town |
|
6. |
Lothal
(Ahmedabad) |
India
(Gujrat) |
1957
A.D |
Famous
port foreign trade |
|
7. |
Alamgirpur
(Meerut) |
India
(Uttar Pradesh) |
1958
A.D |
Jewellery,
utensils, Statues |
|
8. |
Sanghol
(Ludhiana) |
India
(Punjab) |
1968
A.D |
Big
moat with filled water. |
|
9. |
Bnawali
(Hisar) |
India
(Haryana) |
1973
A.D |
Well
planned city Seals and tools |
The total area of this civilization
was 1, 99,600 square kilometers.
Q-2 Answer: - Write a note
about the social life of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Answer: Being a civic civilization, the society of this civilization developed a lot
Was.
I. Most of the sculptures found in the excavations are of women from which it seems that Prabha was the president of the society.
II. The division of society was based
on the actions of the people.
III. People ate two types of food,
vegetarian and non-vegetarian. Wheat, sorghum, Rice, pulses, fruits,
vegetables, milk were the staple foods. Meat from fish Was also used.
IV. Many fry have been found which
suggest that both men and women wore cotton and their clothes. The women wore house
shawls and the men wore granddaughter shawls, their right hand was always
empty. Needles were also found but mostly wrapped in cloth used to go.
V. Both the man and Orra were fond of
jewellery and fashion. Rich People wore gold, silver, and precious stones,
while the poor wore jewelery made of copper, bone, hardened clay, and cheap
beads. The women wore bangles, necklaces and bracelets, while the men wore
bracelets, necklaces and earrings. Women used to adorn their hair more than
they used lipstick and makeup. Some men have beards, some have bandages on their
foreheads were.
VI. People were fond of sports.
Dancing and singing, planning of dice, chess, hunting and watching animal
fights were main sources of amusement. For small children clay toys were made.
Vil. The dead were cremated in three
ways
(A) Babylon cremation,
(B) Buried in ground
(C) Fraction burn like Parsi
community
From the above it is clear that the
social order of the people of the Indus Valley was much better than that of
other civilizations like Egypt and Babylonia.
Question: 3 Write a
note from the economic life of the people of Indus Valley Civilization.
Answer: Economically, the people of
the Indus Valley Civilization were very prosperous.
1. Agriculture and animal husbandry
were the main occupations of the people. A variety of grains, vegetables, and
cotton were grown. The Greeks learned about cotton from the Indians. As the
Indus Valley developed around the Indus River, there was no shortage of water.
People had knowledge of water conservation and irrigation. Indus Valley
Civilization was Famous for Cotton all over the world.
2. The cultivated field which is
obtained from Kali Bangan We came to know they use tools like harrows for
sowing. Tools were made of wood. Wheat and barley were their main crops. Coconuts,
dates, and rice were also grown.
3. Sheep, goats, elephants, camels,
oxen, buffaloes, horses, dogs were kept as pets. Adeqate fodder was available.
4. The people of the Indus Valley
Civilization traded with many parts of the country and Sumer, Egypt
(Mesopotamia abroad) by water and sea. They exported cotton cloth, jewelery,
pearls and ivory products. Animals were also sent out. Gold, silver, necklaces,
and other precious stones were imported. Shilajit was imported from Kashmir on
a series. Marble was procured from Rajasthan, Mysore and gold and silver from
South India. People also worked as goldsmiths, potters, and craftsmen. In short,
people's lived a prosperous life.
Question: 4 What is the
legacy of Indus Valley Civilization? What are the reasons for its decline?
Answer: LEGACY
The imprint of the Indus Valley
Civilization is still reflected in every aspect of our lives. From this
civilization Indians learn to build planned cities, build wide open roads,
provide street lighting, sanitation, sewerage drains, ghats, seals and
sculptures. The art of making children's toys, adorning women's necklaces. The
forms of worship of Goddess Mother, Shivaji, Agni, Jal, Suraj, trees and
snakes, which were worshiped at that time, are still prevalent in Hinduism.
Even today the bronze dancer's posture from Mohenjo-Daro is a style of indian
dance.
Causes of collapse: -
The reason for the collapse or disappearance of the Indus Valley is
understood to be the invasion of foreigners like Aryans war but there is no
concrete evidence. Some historians believe that a sudden flood in the Indus and
its tributaries caused the civilization to disappear. Some believe that
repeated earthquakes or epidemics have wreaked havoc on this civilization. It
is also believed that due to the drying up of the river Saraswati around 10 BC,
people moved eastwards towards the plains of the Ganges. This civilization
collapsed around 1530 BC. Some people attribute its demise due to the plight of
the Dasyu (slave) class of people. In the end we can say that unless scholars
succeed in reading the Indus Valley script in its entirety, nothing can be said
with certainty about the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization.