CHAPTER NO.9 OCEANS
CHAPTER NO.9 OCEANS
Water is the basic need for life while Earth is
known as blue planet because 2/
3 part of earth is covered by this aspect i.e. water
only which looks blue when noticed from Universe. All the water of Earth is
part of hydrosphere and seas, lakes, rivers etc.include init. Hydrosphere
covers 70% part of Earth surface and is one of most important Spheres for
various living organisms and vegetation.
Hydrosphere is continously moving like atmosphere.
Movement is not clear in
lakes and ponds but it could be easily noticed in
rivers and seas. Of the hydrosphere,97.2% of water on Earth is present in
Oceans. Large part of lithosphere lies in Northern
hemisphere. On the other hand 4/5 part of Southern
hemisphere 1s covered by oceans and they cover 3/5 part of northern hemisphere.
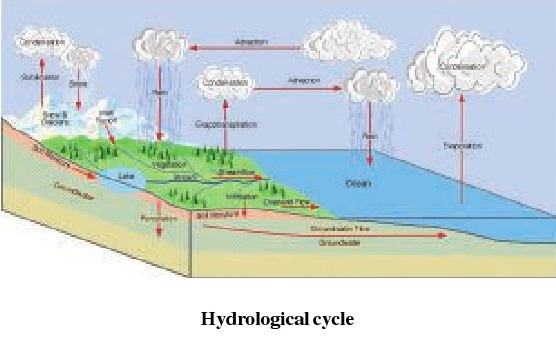
Hydrological Cycle : Continuous exchange of water
takes place between Hydrosphere,Atmosphere and Lithosphere. Water is a unique
liquid which changes its form and place but never stops. Itis because of
evaporation, that water moves into air in the form of vapours and when density
of these vapours increases, clouds are formed.These clouds shed water in the
form of rainfall. Rain water moves into rivers and again
starts its journey towards sea/oceans. During this
process it passes through various stages. This unending process of water is
known as water cycle.
Like land, ocean floors are also deep at some places
and high at others. Mountains,Plateaus, Ridges, Canyons, Trenchs are situated
at the surface of seas also. Collectively these land forms are known as
Submarine Relief.
Ocean Basins may be divided into following four
parts :
Continental Shelf : The part of sea adjoining the
coast is known as Continental Shelf.In other words the parts of continents,
looking like niche of land, which are submerged in sea are known as Continental
Shelf. Rivers continously deposit soils, rocks, stones
etc. on these shelves. These are not very deep
therefore development process of various types of living organisms and
vegetation takes place on the upper layer of water with the help of sunlight.
The depth of continental shelfis not more than 200 meteres
and its slope is angular, to 1 degree. The famous
fishing regions of the world are situated oncontinental shelves. The breadth of
continental shelf varies from some kilomemters to 1000 kilometers.
Continental slope : Continental shelf ends abruptly
and from that point continetal slope starts. Its slope is angular to 2 to 3
degree while its depth varies from 200 meter to 3000 meters. Continental slopes
cover 8.5% part of Oceans. Their slope varies at different places, e.g. at
Calicut coast slope angle varies from 5° to 15° while at Spain coast it is 30
degree and at St. Helenait is 40 degree. This part has less vegetation as
compared to continental Shelf. At some places trenches are situated at slopes,
which
are known as submarine canyons. In Indian Ocean,
submarine canyons are found at mouths of river Ganga and Indus.
Continental Rise : Continental Rise whichis next
tocontinental slope, has very gentle slope which is angular at 0.5° to 1°.
These are not very high. As we go deeper it vanishes into leveled sea bed. At
some places their breadth extends to more than 60 Kilometers.
Abyssal Plains : With the end of continental rise
and where ever only continental slope exists, at the end of slope, “Sea Plains’
start which are known as ‘Abyssal Plains’.These are levelled plains and their
slope is less than 1 degree. Their depth varies from
2000 to 6000 meters. Red soil of volcanoes and
remains of living organisms are found in these plains.
Submarine Ridges and Rises : Like lithosphere,
mountain ranges are situated in the sea also. These extend upto thousands of
kilometers and they cover 1/3 part of sea bed. These are also known as
Mid-Oceanic Ridges. At some places these look like high
mountains and at some places these are situated in
the form of Plateau.These areas experience continous earthquakes and volcanic
eruptions resulting in the formation of various physical features. Peaks formed
by volcanic eruptions rise above the sea level to form Islands in the seas and
oceans. Hawaii and Tahiti are their finest examples. Some times the upper parts
of high peaks are flattened. These are known Guyots or Table Mounts.
The Ocean Deeps : The deepest part of the seais
known as Ocean deep. Itis atype plain beneath the sea. These deep plains may be
deep, long or levelled, all lie beneath the sea. The deepest deeps are found in
Pacific Ocean on our mother Earth.Marinais the deepest trench whichis situated
in South Western Part of Pacific Ocean.Its depth is 20 percent more than
world’s highest peak i.e. Mount Everest, that means if “Mt. Everest’ is placed
into this trench, its highest point shall still remain 2 Kms.
beneath the waters of pacific Ocean.
Six deep trenches are found in Indian Ocean. Among
these, Java trench or Sonda
Trench is 7,450 meter deep.
Floors of Oceans
According to International Hydrographic
Organisation there are five major Oceans :
1. Pacific Ocean
2. Atlantic Ocean
3. Indian Ocean
4, Arctic Ocean
5. Antarctic Ocean
While we classify “World Ocean’ into four parts 1.e.
Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Oceans,Indian Ocean and Arctic Ocean.
The floor of he Pacific Ocean, Shape and Size :
This is the largest ocean of the world. Its average
depth is 4280 meters (14040 feet) or 2,333 fathoms. Its total areais
16,52,50,000 square kilometers which is 1/3 part of total area of Earth.
Pacific Ocean covers 46% part of world Oceans. This Oceanis touched by five
continents. At equator its extent is more than 16000 kilometers.Maximum
typhoons and active volcanoes are found in this ocean.
It has triangular shape and Bearing Strait is
situatedinits north. Asia and Australia form its one part and other partis
formed by North America and South America. Antartic Ocean is situated towards
its south. Size of Pacific Ocean is decreasing by 2-3 cms every year on the
other hand the size of Atlantic Oceanis increasing.
Continental Slope : Continental Slope of Pacific
Ocean is quite broad along Asia,
Indonesia and Western Coast of Australia. Its
breadth extends from 100 meters 150 meters. Many islands are situated along the
continental slope of Pacific Ocean e.g.Islands of Japan, Phillipines, Indonesia
and Newzealand. Its breadth becomes narrow along the western coast of America,
where its average breadth is 100 meters.Overall, more than 20,000 islands are
situated in this Ocean. Islands situated in its
north and continental slope are formed by volcanic
eruption. Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa are the major peaks situated on these
islands, height of these peaks, is 4213 and 4168 meters respectively. In
northits depth extends from 5000 meters to 6000 meters.Various trenches are
found in this ocean e.g. Aleutian, Kune, Japan and Bonin. Most of the trenches
are situated along the Islands. Celebes Sea, Coral Sea, East China Sea,Yellow
Sea Tasman Sea etc. are situated towards its west coast. In the westen part
Malacca Straight connects the Pacific and Indian
Ocean.reat Pacific - Garbage Patch :Every year, 90 billion kilograms of Plastic
is produced nthe world. Of this 10% plastic is disposed off into the Pacific
Ocean in the form of
aste. This waste is termed as the “Great Pacific
Garbage Patch’. It is deposited i hose parts of sea where speed of winds is low
and waves are weak. Its small part sinks down and rest of it floats. Itis very
dangergous for living organisms and vegetatio pf sea.
Floor of Atlantic Ocean, Shape and Size :The shape
of Atlantic Ocean resembles with English language Roman Script alphabet ‘s’. It
covers 22% part of the Earth and its average area is 8,24,00,000 square
kilometers. Its average depth is 3,339 meters (10,955 feet) or 1826 fathoms
than that which is less Pacific Ocean. Its deeptest part is ‘Milwanke-deep’ (8380
meters) which is situated in the north of “Puerto Rico’.
Its breadth is 1530 nautical miles (between Brazil
and Sierra Leone) and in south it is 3450 nautical miles or 6400 kilometers.
The eastern side of this ocean 1s connected with North and South America and
its eastern side is connected with Africa and Europe.
Continental Slope : It is quite wide at
eastern and western coasts and is situated along the
coasts of America and Europe. The slope is quite narrow between South America
and Africa while major broad continental slopes of the world are around New
Foundland and British Isles. Grand Bank and Dogger Bank are situated here which
are the
most popular places of world for fishing. The
breadth of continental shelf extends from 250 to 400 Kilometers near the coasts
of North Eastern America and North Western Europe.
Mid Atlantic Ridge : Deep ‘sea plains’ are found in
this ocean, which donot have equal depth. Their elevation towards central part
to eastern and western coasts is quite gentle and a long mountain has been
formed in the centre which is like andge. This is
the speciality of Atlantic Ocean floor. This
mountain extends from Greenland to Bouvet Islands and vertically divides this
Ocean into two parts. Its average height is 14000 .meters and itis 14000
kilometers long. Its large part is covered by water but some of its parts are
visible above the sea in the form of islands. Some of these islands are
Ascension Island, Tristan da, Cunha, Azares, St.
Helena and Gough. These are all volcanic islands and their various small peaks
attain the form of islands. The upper line of this mountain is quite wide at
55° North latitude, whichis known as Telegraphic Plateau. This is also known as
under water nse. Various seas and bays are situated on its coast. On the
western coast of ocean ‘Hudson Bay’ and “Basin Bay’ are situated
and on the eastern coast ‘Northern Sea and Baltic
Sea are situated.
This Ocean does not have large number of trenches.
Around 19 trenches are 5500
meter deep at average and 2 trenches are 7000 meters
deepin this Ocean. Many deep
sea parts e.g. Labrador Basin, North Eastern
Atlantic Ocean Basin, Argentina Basin and Agulhash Basin are part of Atlantic.
Floor of Indian Ocean, Shape and Size :
Although this oceans smaller than Pacific and Atlantic
Oceans yet it is more important for us. Itis situated in the south of our
contry and its name is also based on older name of our country. The total area
of this ocean is 7,34,25,500 square kilometers and its average depth is 3960
meters. [tis almost triangular in shape and is surronded by Iran, Pakistan,
India,
Bangladesh, in north and north east, by
Australia in the east, by Antarticain the south and
in west, by Africa.
Continental Slope : Average width of its continental
slope is 75 miles (120 km). It is 190 miles (1300 kms) wide near Mumbai,
whichis almost maximum. Tropic of cancer is the upper boundary of this Ocean
and 90 percent part of this Ocean lies below the Equator i.e. in Southern
hemisphere. Its bedis completly flat. Red sea and Persian Gulf are situated in
its North, Arabian Seain North West, Andeman Sea and Bay of Bengal are situated
inits North east. Trenches are very rare in this Ocean. Sunde trench is
situated in the south of Java. Which is 8152 meters
deep. There are many under water mountains, situated on the bed of Indian
Ocean. Longest mountain (Submarine Ridge)extends from cape C omorin to
southwards (Towards Antartica). Itis quite wide but it
is not very high. Itis wider than mid Atlantic
Ridge. Its elevated (higher) parts are present in the form of islands e.g.
Chages mountain inits north, St. Paul Ridge and New Amsterdem *Medagaskar’ and
“Sri Lanka’ are the largest islands of Indian Ocean.
(i) Try to find out, Indian Ocean is connected with
which sea through Suez Canal?
(ii) Find out why the Andeman Nicobar Islands have
shifted 1.25 meters towards
South West and submerged in sea by | meter?
Floor of the Arctic Ocean, shape and Size :Its size and depthis less as compared to other oceans. Actually it is circular and surrounds the North Pole. Its average size is 1,40,56,000 Sq. Kms. and its Coast line is 45390 kilometers. The Artic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia, North Amenica, Greenland and various islands.Various islands are found in this ocean namely, New Syberian islands near Canada, Navaea and Jalmaya are major islands while. Barents Sea, Beaufort Sea, Chukchi Sea, East Siberia Sea,Green land Sea, Kara Sea, White sea,Hudson Bay and Baffin Bay are also found in this ocean.
It is connected with Pacific Ocean by Baring Straight and connected with Atlantic Ocean with the help of Greenland Sea and Labredor Sea. Its long submarine Ridge is known as Lomnosone Ridge.
The layer of ice of this Oceanis melting
continuously slow pace and there is a possibility that major changes to occur by
2040.
Temperature of Ocean Water Temperature of land
increases and decreases at faster pace as compared to that of sea
or water while the temperature of sea waters is not
same and constant at all the places.It is higher near the Equator and low near
the Poles. The upper most layer of sea water is 500 meters thick (deep) and its
temperature varies from 20° to 25° celcius. Thickness of second layer extends
from 500 meters to 1000 meters and itis known as Thermocline.
Because of its deepness, temperature starts
decreasing and moreover the flow of cold waters in its lower part, the
temperature decreases further. In simple words the temperature decreases with
the increase in latitude and depth but does not reach at freezing point.
Factors Affecting Distribution of
Temperature
1. Latitudinal extent of Sea; As we move from
Equator to poles, temperature of sea water decreases. Temperature remains high
at Equator and gets low towards poles,which affects temperature of sea water.
2. Albedo of the Ocean surface at varving times :
Albedo of those water bodies is higher which have low mobility of water. Higher
the Albedo, lower will be the temperature. Lighter and whiter bodies have
higher Albedos than darker, black bodies.
Albedo : It is the fraction of solar energy
(Shortware rediation) reflects from the Earth back into space. Total Albedo of
Earth is 35%.
3. Ocean Currents : Hot water currents increase the
temperature and cold water
currents decrease the temperature. Temperature of currents moving towards poles from Equator is high and on the other hand the temperature of currents moving towards Equator from poles is low.
Hot water
currents of Gulf Stream increase the temperature of western coast of
Europe.Cold water currents of Labredor Sea decrease the temperature of North
Eastern Coast of America. So, the temperature of currents affects the
temperature of sea water.
4. Prevailing Winds : Oceanic waters become mobile
with the movement of winds.This mobility results into mingling of cold and warm
waters. Winds pressurise Sea waters to flow in the direction of their own flow.
Hence, generally speaking waters start flowing from regions with lesser
temperature to regions with higher temperature.
5. Effect of Adjacent land Masses : The temperature
of sea increases in summer,
which is surrounded by land masses and it decreses
in winter. The temperature of ocean near Equator rises upto 26°C in summer and
in Red seait rises utp 30°C.
Try to find out :Oceans in Northern hemisphere
acquire more Solar energy as comared to oceans in Southern Hemisphere, Why ?
6. Salinity : If the sea water is more saline, its
temperature will be higher because highly saline water contains more energy on
the other hand the temperature of less saline water is low.
7. Ice flows and Ice bergs : These are made up of
ice because of this they decrease the temperature of sea. Their affect is very
common in polar regions.
Do you know ?
Some ice bergs from North polar and South polar
regions start floating towards Equator in their respective summer seasons.
These icebergs are known as ice flows also.Salinity of the Ocean Waters Sea
water has brackish taste because of the dissolved salts init. This water 1s not
good for human consumption and it may be used only after distillation.
According to the scientist Dittmar, 47 different
types of salts are present in sea. Some of the important elements are given
below:
Various elements of these types are found in sea but
Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (C1)are the most important elements, they form sodium
Chloride. Its common name is “common salt’ and ‘table salt’. The average
salinity of oceanic waters is 35%, which means that 1000 grams of water
contains around 35 grams of salts. High salinity meter
starts at 24.7% salinity measure. Salinity varies in
different parts of oceans and seas.Regions, where evaporation is high, salinity
is also high on the other hand where the
amount of fresh water and rain water is more,
salinity is less.
Salinity of sea water increases as we move from
Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of
Capricon to Equator. On the other hand it decreases
toward poles. Rivers bring large amount of salt into sea because of the erosion
and friction process which they perform in their valleys. Inspite of this,
various types of living organisms and vegetation naturally
increases the salinity of sea water. In a map
showing salinity of oceanic waters, lines joining places with same note of
salinity are known as Isohalines.
Try to find out :
Salinity of Dead Seais highest in the world, Why ?
Do you know :If we spread all the slat of
hydrosphere, on the Earth, the layer formed will be 150 meter thick, it shows
that 1 kg water contains 35 grams of salt init.This measurment is generally
made with the help of Part Per Thousand i.e. PPT which is represented as %, (per
thousand).
Factors affecting Salinity :
Following factors affect Salinity of Oceanic waters
:
1. Evaporation : When water moves into atmosphere in
the form of water vapours,
that process is known as evaporation. Itis directly
related with temperature. Where the evaporation is high, salinity of sea water
is also high.Try to find out; Why the water at Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of
Capricorn is highl
saline?
2. Fresh Water : Fresh water affects the salinity
toa great extent. Salinity of that sea water is low which receives high amount
of river and rain water and on the other hand where the emergence of rain and
river water is low, salinity will be high.
3. Ocean Currents : Hot water ocean currents,
increase the temperature of water and cold water currents decrease the
temperature. Because of this currents moving towards Poles from Equator bring
highly saline water and on the other hand currents moving toward Equator from
Poles bring water which have low salinity.
4. Winds : High speed winds result in the movement
of water towards their flow, which affects the salimty of water.
Let us know:Itis because of human activities that
one third Carbondioxide mixes up in sea water.Sea waters are becoming acidic
because of atmospheric pollution and pollutents orignated by factories. All
this is affecting the not only “marine life but overall flora
and fauna also.
Ocean Currents :Sea water is a liquid whichis not
stable and free to move. This mobility of sea waters is divided into three
parts :
1. Tides
2. Waves
3. Currents
Currents are defined as those waves on the surface
of sea water which move horizontally.Water moves from one place to another like
a nver, actually it moves in a specific direction. Name of current is based on
their direction. Acurrent 1s actually that water
which flows in specific direction only. There are
various types of currents in Oceans,which move and shift water from one place
to another. These are affected by the size,depth and structure of sea. Water
flowing as current remains stable at the both ends and moves faster than the
river water in middle part and flow is much deeper and large also.
Ocean Currents : The length of currents extends upto
1000 Kms and they may be 200 Kms broad. Their speed is faster than that of
rivers. In each current speed of water varies from 2 to 10 Km/Hr. They move
towards a particular direction for long time and collectively form a big flow
called ‘Global Conveyor Belt’, which affects the Global climate. e.g. The
temperatures of Gulf stream and Humbolt current make their surroundings warm
and cold respectively. Ports of eastern North America do not freeze in winter
due to warm effect of Gulf Stream where as tempratures in Lima and Peruis lower
than their surrounding areas. Although these are situated on tropical latitude
but still their temperature is low.
et us know :S peed of Current is measured in Knots
and 1K not = 1.85 Km/Hr (1-15 miles/Hr)233
Oceanographers have classified currents
on the basis of various methods.
These are given below :
Types of Currents:
(a) Periodic Currents : Currents which change their
speed and direction after particular fixed time are known as peridic currents.
(b) Seasonal Currents : Those currents which change
their speed and direction with changing season.
(c) Coastal Currents : Those currents which move on
the outer side of the sea coast.
(d) Long shore Current : Those currents move along
the sea coast as these are
produced when the waves strike of the coast, these
flow close to coast and upto long distances.
(e) Off shore Current : These are produced at a
distance from the coast.
(f) Inshore Current : This type of currents are
produced near to the coast.
(g) Drift : Those currents which get broader under
the affect of prevailing winds are known as drift. The velocity of the drift is
less than 24 km aday.
Namely, for example
(i) North Atlantic Dnift
(i) West Wind Drift
(h) Streams : These are large size currents, having
large volume of water moving.
Types of Curents on the basis of
Temperature :—
(a) Hot Water Currents : The currents which move
from warm regions to cold regions are known as hot water currents.
(b) Cold Water Currents : Those currents which move
from cold regions to hot
regions are known as cold water currents.Causes of
origination of the Ocean Currents :There are various reasons because of which
ocean currents are formed; Roation of Earth, Gravitation, Heat of Sun,
Temperature difference, Salinity, Density of water,
Melting of Ice, Instant change in weather, Direction
and size of coast etc.
Let us examine these reasons in detail
:
(i) Prevailing Winds : These winds are permanent and
always flow in one direction.With their friction they move sea water because of
which currents are formed.Trade winds blow towards west between 30° North and
30° South of Equator. Because of this currents move from east to west in the
north and south of Equator i.e. in at Tropical region. Similarly, Western winds
blow between 40° North to 65° North and 40? South to 60° South latitudes
(Temperate region). They move from west to east because of this they are known
as Western Winds. Currents moving from west to east
are not known as western currents. They are known by
the name of that directionin which they are moving. In Indian Ocean direction
of Monsoon winds change with the change in Weather.
(ii) Temperature : Currents find their birth in
variation of temperature of Oceanic waters. Currents move in North-South
direction because of temperature difference between Equator and Polar regions.
In other words we can say that when heavy and cold water of Polar regions
settle down, hot water starts moving from Equator to Poles for aquiring the
empty space. Because of this hot water currents move from equator to poles
causing birth of hot and cold water currents because of the difference in
temperature.
(iii) Density of water : Density of saline water 1s
more than the density of clean water.Highly saline water settles down because
of its weight. To fill that space clean water moves toward the region,
resulting in the formation of current. Salinity of Medittrainian
sea is higher than that of Atlantic Ocean because of
this a current moves from Atlantic Ocean to Medittrainian sea along side upper
water.
(iv) Evaporation : Evaporation reduces the sea level
as water evaporates in this process.As soon the water level decreases, flow of
water from other regions begins towards decreased level region. This forms a
‘current’.
(v) Rotation : Earth rotates on its own axis because
of which ‘centrifugal force’ 1s produced. Under the affect of this force,
flowing water opts a circular path, which is known as Gyre. The movement is
clockwise in Northern Hemisphere and anticlockwise in Southern Hemisphere.
Currents in “N. Hemisphere’ move towards right and in *S.Hemisphere’ currents
move towards their left. Winds also turn on the basis of this *Farrel’s law’ .
In Atlantic Ocean, Western Winds produce acurrent called ‘Gulf Stream’.
Do you know:Gulf Stream is 50 miles wide and Its
speed is 5 miles per hour.
Currents of Atlantic Ocean :In the Equatorial region
of Atlantic Ocean, Trade Winds give direction toimportant currents. In simple
words, it is becasue of Trade Winds that water of Equatorial region starts
flowing towards west,
resulting in the formation of currents. These are
hot water currents. Some of them move towards North from Equator and others
move towards South.Anant current starts flowing from west to east named
as Equatorial Counter Current between North Equatorial
Current and South Equatorial Current.
Currents of Northern Atlantic Ocean :
North Adantic Ocean Equatorial Current : Flows from
western coast of Africa to
Central American Island along the equator due affect
of Trade winds.
Antilles Warm Current : Antilles Current is actually
south Atlantic Current which
finds its origin under the effect of Trade winds in
Southern Atlantic Ocean near the Equator at Western African Coast. Flowing west
wards it reaches upto Cape-de-Sao-Rogue i.e. eastern end of Brazil. Here this
current is divided intotwo parts. Southern part starts flowing southwards while
its northern arm contributes its warm water to
North Atlantic Equatorial Current.
Florida Current : This current moves along the South
Eastern Coast of USA. This is a hot water current.
Hot Water Current of Gulf : From Cape Hateras to
Grand Bank this current is
known as Gulf stream. Itis 45 Kilometer wide water
channel and it moves at the speed of 6-7 km/hr. This hot water stream dEflects
towards east due to the affect of western winds and rotation of Earth and after
crossing Atlantic Ocean it is known as Hot water current of North Atlantic.
Norway’s hot water Current : In eastern part of
Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic
current is divided into two parts. The part which
deflects towards north, enters into Arctic sea while moving along the coast of
Norway. Thisis known as hot water current of Norway.
Canaries Cold Current : The other part of North
Atlantic current deflects towards west and reaches upto canary Islands. Due to
rotation of Earth and coastal obstacles/hindrances, second branch of hot water
current of North Atlantic deflects towards south. It moves along the eastern
coast upto Spain and Azores in the form of new stream. This is known as cold
water current of Canary. It moves further and conjugates
with the hot Equatorial Waters. Thus North Atlantic
Ocean currents complete their one circle flowing clockwise and ending upin
equatorial waters at Sargasso Sea. The name of ‘Sargasso Sea’ is derived from
the Oceanic Algae Or Sea weeds whichis brownin colour and known as ‘Sargassum’.
The area of Sargasso Seais taken 11000 square Kms.
Labredor Cold Current : This current moves towards
New Foundland through Bay
of Baffin. It moves along the eastern coast of
Canada and conjugates with warm Gulf stream. This conjugation causes dense fog
near New found land.
Southern Equatorial Current : As this current moves
toward west, it gets divided into two parts at the coast of Brazil. One
deflects towards north and other starts moving along the coast of Brazil. This
is known as hot water current of Brazil.
Cold Water Current of Southern Atlantic Ocean : Hot
water current of Brazil
starts moving towards east due to affect of Western
winds. When this current moves toward east, itis known as cold water current.
Benguela Cold Current : Due to the rotation of
Earth, some part of current of southern Atlantic Ocean deflects towards north
and when it strikes with the Western Coast of Africa, water starts flowing
towards North. At that point itis known as Benguela Cold
current. It conjugates with the Equatorial current
and completes its cycle.
Currents of Pacific Ocean :Currents of Pacific Ocean
also move like the current of Atlantic Ocean.
Northern Equatorial Current : Due tothe affect of
Trade winds these currents begin from the western coast of central Amenca and
reach upto Phillipines islands while moving from east to west.
Southern Equatorial Current : In south, Southern
Equatorial Current moves towards west. Between these two currents an opposite
current moves towards east. This is also a hot water current. From Phillipines
islands, North Equatorial Current moves towards north along the coast of Taiwan
and Japan. At this point, this is known as Kuroshio Current.
North Pacific Current : Kuroshio current is divided
into two parts while moving
along the coast of Japan. One of its branch moves
along the eastern coast and another branch moves along the western coast.
Flowing along the coast of Japan, both of these currents start flowing towards
North-East jointly, under the name of Warm Water Drift of Pacific Ocean.
Cold water Current of California : North Pacific
Current is divided into two parts at the western coast of North America.
Northern part flows anti clockwise along the coast of British Colombia and is
known as ‘Alaska Current’. This is a hot water
current and due to this current water does not
freeze at the coast of British Colombia and Alaska. Its second branch deflects
towards south along the coast of California.This is also known as cold water
current of California.
Oya Siwo Current : This is acold water current which
begins from Bearing strait and moves from north to south upto east of
“Kamchatka Peninsula’
Okhotsk Current or Cold Kurile Current : This
current moves along the eastern
coast of Sakhalin islands and conjugates with the
Oya Siwo Current near Hakkaido
island of Japan. Here Oya Siwo Current joins it and
its water strats flowing beneath warm water of Oya Siwo because of which fog is
formed at this point. Joining of hot and cold currents results into production
of planktine, food for fish.
Southern Equatorial Current : This is a hot water
current which moves along the
coast of Central Americain East to the eastern coast
of Australiain west. It flows south wards along eastern coast of Australia and
1s known as warm current.
Southern Pacific Drift : Eastern Australia Currents
move from west to east near Tasmania. Here, these are known as Southern Pacific
Currents. This current deflects towards north at the south western coast of
South America and moves further along the coast of Peru. This is also known as
cold water current of Peru. In this way acycle is completed. Because of this
cold water current Chile and Peru receives very low rainfall at their coastal
regions.
Currents of Indian Ocean :Currents of Indian Ocean
are highly affected by Monsoon winds. Direction of Monsoon
winds changes in summer and winter season because of
which direction of currents alsochange. In the north of Indian Ocean, more land
mass is found and in southern portion of Indian oeccan, more open seais found.
This snatches an opportunity from northern region to have acycle of currents
like that in other two oceans while Southern
Indian Ocean enjoys same current cycle.
Currents of Northern Indian Ocean : In winters,
northern equatonal current
deflects southwards while moving from east to west.
Thisis known as North
Eastern Monsoon drift. This drift begins from
Malacca strait enters into
Arabian sea while moving along the coast of Bay of
Bengal. It deflects
southward near Bay of Aden and starts moving from
west to east and completes its cycle by conjugating with Opposite Equatorial
Current.Insummer, monsoon winds flow in south-east direction because of which
some part of
Southern Equatorial Current and Northern Equatorial
Current start moving along the coast of Africa. This is also known as “Current
of Somali’
Do you know:
In ancient times Indian Ocean was knownas Ratnakara,
which means mine of Gems.
Try to find out :In which months Monsoon wind flow
South West and in which months they flow
North-East ?
South Western Monsoon Drift : Currents of Somali
creates acycle around Indian
sub continent due to the affect of South West
Monsson Winds. These are known as
South Western Monsoon Dnift.arious rivers flow to
Indian Ocean, following are a few major out of them major Zambezi, Indus,
Narmada, Ganges, Brahamputra, Jubba and Irrawaddy.
Currents of southern Indian Ocean :
South Equatorial Current : South Equatorial Current
moves from east to west as that of South Pecific Current.
While moving further it gets divided into two parts.
One of its branch deflects towards the south of Madagaskar island and other
moves along the coast of Mozambique. This is also known as hot water current of
Mozembique. When this current moves along the eastern coast of Madagaskar it is
known as Madagaskar hot water current.
Agulhas Current : This hot water current has been
formed by the conjugation of hot water currents of Madagaskar and Mozambique.
West Wind Drift : Because of western winds, Agulhas
current, deflects towards north at the southern end of Africa. While moving
further it conjugates with cold Antartic current.
West Australian Current : It moves from west to
east. It moves along the southern coast of Australia and its second branch
deflects towards north from the western coast.The second part is known as cold
water Current of Western Coast. While moving further it conjugates with the
Southern Equatorial Current and completes the cycle of
Southern Indian Ocean.Effects of Currents Ocean
Currents leave intense effect in coastal regions, islands, economical
activities,weather, agriculture etc.
Let us study about this in detail :-
Hot water currents help in rising the temperature.
Kuroshi wo current and Gulf stream modify the weather of Southern Japan and
Eastern America respectively. Ports of Western Europe are used as trade points
for whole of the year becasue hot water does allow water to freeze in any
season. Cold water currents decrease the temperature coast of Labredour is
freezingly covered by ice because of cold water current.
Currents also effect the amount of rainfall. Hot
water currents increase the rainfall because they bring winds along with them,
laden with water vapours. North America, Ireland,
Britian and south India receive rainfall because of
this process. On the other hand Atacama desert remains dry because cold water
currents donot play any role in occurance of rainfall. Due to this various
deserts are situated on the western coast of Australia, South America and
Africa.
Try to find out :Where is ‘Atacama desert’ situated
?
Conjugation of hot and cold water currents helps in
increasing the development rate of ‘Plankton’, whichis a diet of fish. This
conjugation takes place of eastern coast of North America, where New Found land
current and Labredour current enjoined making
ita major fishing bank of world.
Superior quality fish are found in cold water
currents. When these currents move towards regions with high temperature, they
carry fish with them. This movement boosts the fishing trade. The direction of
currents helps in saving fuel and time also while similar direction encourages
speed of moving ships.
On the other hand conjugation of currents forms
dense fog which creates problem for marine navigation. Sometimes ships are not
able to move because of this fog. This whole situation effects the economic
activities of respective areas.
Waves
Water of Oceans never stops. It moves in the form of
waves in the direction of winds.Waves are the forward movement of ocean’s water
due to the oscillation of water particles by the frictional drag of wind over
the water’s surface. The peak of the wave is known as crest and lowest point is
known as trough.
Waves donot move the water horizontally. We can
prove this with an experiment. Fill a tub with water and make a disturbance
init with your hand, now put acork in it.Notice it for some time, you will find
out that cork moves up and down without changing its position. With the help of
this experiment we can say that water doesnot move horizontally.
The wave length or horizontal size of wave is
determined by the horizontal distance two crests or two troughs. The vertical
size or height of wave is determined by the vertical distance between crest
while direction and speed of waves is not same always and it
depends upon the speed of winds. Wave period is a
length of time it takes for a wave to pass a fixed point (crest to crest).
We can find the speed of wind with the following
method:
Try to find out :What is th eeffect of waves on the
depth of sea ?
Wave length
ave Velocity = Wave Period
The effect of winds reduces over the waves and
currents with increase of depth. Waves depend on the speed of winds. High speed
winds increase the power and height of waves. Sometimes speed of wind reduces
due to barries, this also effect the waves.When a wave breaks water moves with
turbulent speed like a river towards coast which is known as swash/surge.
Sometimes it moves sand, rock particles towards coast. The decending of this
surge is known as back wash.High speed waves which move for long time are known
as swell. These are also known as capillary waves. Their wavelength is more
than 100 meters. As waves approach land masses, the wave base begins to contact
the sea floor. The friction slows the circular motion of wave’s base. This is
known as breaker. These type of waves when move towards shore these are known
as ‘surf’.
“Erosion’ is always high and fast at soft sea coasts
which forms various types of land forms.
Tsunamis
These are also known as seismic sea waves or long
wavelength sea waves.
These are formed due to volcanic activity or
Earthquakes in sea, Asteroid, Displacement on the surface of water because of
break down of ice bergs etc. They may have wave length of 100 km and their
speed may vary from 600 to 800 kn/hr. Their height may grow more than 15
meters. (50 feet). In 2004 these waves resulted in the huge loss of
life and property in south India. A large plate
(hence large wavelength) of the earth's crust creates these waves by displacing
water and the energy liberated is huge. Wave amplitudes are small (0.1 — 1 m)
but the wavelength is large, typically 100 to 1,000 km.
Oscillations of water particles are not just
restricted to the water surface but are distributed in the entire depth. We
cannot create such waves by a paddle. Because of the large volume of water
involved, energy of tsunami waves is large even though the amplitudes are
small. This is why itis difficult to observe the height of tsunami waves in
the open sea but close to shore they become
disastrous.
Tides
Tides refer to the periodic rise and fall of Oceanic
water. This movement takes place because of gravitational pull of Sun, Moon and
Earth. Height of tide depends on the position of Moon. Affect of gravitation is
high because water particles are present in
Seain liquid form. Tides rise twice in aday with the
gap of twelve hours approximately.To be more exact the difference may be put as
12 hours and 25 minutes. Basic reason behind this time difference is the
difference of time taken by rotation of Earth and one
revolvation of Moon. The Earth takes 24 hours to
complete one rotation on its axis while moon takes 29 days and 12 hours to
complete its one rotation around the Earth.Result of this time difference is
that any place on Earth faces the same to moon not after
each 24 hours but 24 hours and 50 minutes. Hence,
tides occur after 12 hours and 25 minutes each. Itis the gravity of Earth which
gives birth to the tides along with effect of
rotation. When atide rises on the portion of Earth
facing moon, the opposite side of Earth also gives rise to tide due to
rotational effect of Earth.
The average height of tide is 0.55 meters but sometimes it may vary from 2 to3 meters.Sun also produces tides, these are known as Sun tides. Their height is less than lunar tides (Tides produced by Moon)
Tides based on the location of Earth, Moon and Sun.
1. Spring Tides : These tides occur when the Sun and
Moon are directly in line with Earth. These tides occur twice a month, at full
Moon and new Moon.
2. Neap Tides : Spring tides and Neap tides occur
with the difference of seven day.That means the days between full moon and new
moon. Basically Sun, Earth and Moon are positioned so on the 7th and 21st day
of lunar month that these callestial bodies form aright angle. The effect of
these bodies is seen against each other which results into Neap tide as
compared to normal tidal activity.
For once in a month moon draws nearest to the Earth
during its revolvation which is known as ‘Perigee’. While after two weeks it 1s
situated farthest to the Earth known as *Apogee’.
Importance of Tides :Depth of water increases near
the coastal area because of spring tides. Because of this
big/heavy ships can easily move towards port. Kandla
of Gujarat and Diamand Harbour of Bengal are its major examples. Tides act as
barriers in the deposition of soil and helps in desiItation at mouth of rivers.
Power is generated with the help of tides. Fishing boats also take help of
tidal activity while entering the ports or getting out of it.
EXERCISE
1. Write the answer of the following
questions in few words :
(a) What is the percentage of area covered by
hydrosphere on Earth ?
(b) Why Earth is called blue planet ?
(c) Which unit is used for measuring depth of sea?
(d) What is Plankton ?
(e) Write the name of any trench of Indian Ocean ?
(f) Name biggest ocean of the world.
(g) Agulhas Current flows in which ocean ?
(i) Indian Ocean (ii) Atlantic Ocean
(iii) Arctic Ocean (iv) Pacific Ocean
(h) Name deepest trench of Pacific Ocean.
(i) What is average depth of Indian Ocean ?
(j) With which continents Pacific ocean touches ?
(k) What is Tsunami ?
(l) Temperature decreases with increase in depth and
latitude, comment.
(m) What is average temperature of oceans near
Equator in summer ?
(n) Is Gulf Stream a hot water current ?
(0) What is Albedo?
(p) What is Salinity ?
(q) On which latitude, Salimity is maximum ?
10°N to 15°N
15°N to 40°N
60°S to 70°S
(r) Which unit is used to express salinity of
oceanic waters ?
(i) per 10 grams.
(i1) per 1000 grams.
(11) per 100 grams.
(s) Name factors effecting salinity of oceanic
waters.
(t) What is difference between Salinity and
Temperature ?
2. Answer the following in few
sentences :
(a) Define Continental Slope
(b) What is difference between Guyots and Mounts ?
(c) What do you understand by Water Cycle
(d) Explain Difference between Abyssal plains and
Continental Slope.
(e) What do you mean by Ocean Currents ?
(f) What are the reasons behind formation of Ocean
Currents ? Explain any four reasons in detail.
(g) Explain any two hot water currents of Atlantic
Ocean.
(h) What is the reason behind the presence of fog at
New Foundland Coastal
region?
(i) What is the difference between Ocean currents
and Tides ?
(j) Why does the temperature of sea changes with the
variation in depth? Write about thermal layers also.
(k) What is the effect of currents on temperature ?
(l) Write in detail about factors affecting
distribution of temperature of Oceanic Waters?
(m) What do you mean by Waves ?
(n) What are Tsunami Waves ?Wnite a note about the
distruction they have caused
at any place ?
(0) What is the length of waves ?
(p) What is the height of waves ?
(q) What is the relation between waves and winds ?
Which formula is used to
study the velocity of waves ?
(r) Define ‘Surge’.
(s) When do the tides occur ?
(t) How many times do the tides occur in a day and
what 1s their magnitude ?
Explain.
(u) What is the average height of Tide ?
(v) What is the difference between Spring tides and
Neap tides ?
3. Answer the following in detail :
(a) What is Ocean basin ? Explain in detail with
examples.
(b) Write a note on Wetands of Punjab. Suggest ways
to check their pollution.
(c) What is the effect of Monsoon winds on the
currents of Indian Ocean ?
(d) Write in detail about the effects of Ocean
Currents over their surroundings,
with examples.
(e) Show the hot water and cold water currents on
the world map. What is the
effect of Currents on the surrounding area?
(f) What is the procedure of tide formation and What
is its importance ? Explainin detail.