2 BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION#
CHAPTER NO.2 BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
A6
CLASSIFICATION is the process
of grouping organisms into convenient categories based on some easily
observable characters.
NEED OF CLASSIFICATION
1.It makes study of various living organisms easy.
2.Identification of organisms becomes easy.
3.It helps in Knowing relationships among different
groups of organisms.ARISTOTLE was the earliest to attempt a scientific basis
for classification. He classified plants into trees, shrubs and herbs. He
divided animals into two groups: -
1. Animals which had red blood 2. Animals which had
not red blood.
LINNAEUS gave the Two Kingdom System in which all
organisms have been
classified into two kingdoms - Animalia and
Plantae.This system did not distinguish between prokaryotes and
eukaryotes.Classification systems for the living organisms have undergone
several changes
over time.
Today FIVE KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION is
followed.:-
It was proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. The five
kingdoms are :
1.Monera
2.Protista
3.Fungi
4.Plantae
5.Animalia
Main criteria for classification in this system are
:-
1 COMPLEXITY OF CELL STRUCTURE :--Cells
are of two types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic.Prokaryotic cells do not have true
nucleus, membrane bound organelles, spindle apparatus and 70S ribosomes are
present.
Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, membrane bound
organelles, spindle apparatus, 80S ribosomes are present in cytoplasm and 70S
ribosomes are present in mitochondria and plastids.Prokaryotes are placed in
Kingdom Monera.Eukaryotes are placed in KingdomsProtista,Fungi,Animalia and
Plantae.
2 .COMPLEXITY OF BODY STRUCTURE - Organisms have two
types of body structure - Unicellular and multicellular. Unicellular
organisms placed in kingdom monera(prokaryotes )and
protista(eukaryotes)Multicellular organisms are placed in Fungi,Animalia and
Plantae.
(a) Autotrophy
(b)Heterotrophy
(a)Autotrophy :-These organisms prepare their own
food from inorganic raw material.|t is further of two types :
*«Chemoautotrophic-Energy released from chemical
reactions is used to synthesize organic food from organic raw materials.
* Photoautotrophic- Radiant energy is used to
synthesize organic food from inorganic raw material.
(b)Heterotrophic - Organisms take readymade food
from other organisms.
Types eHolozoic (Ingestive)-Solid food is taken and
digested inside the body.eSaprophytic -Absorption of soluble organic remains as
food.
eParasitic-Food is absorbed directly from other
living organisms
4. PHYLOGENETIC RELATIONSHIP
:-The earliest living forms produced prokaryotic organisms (Monerans).Monera
gave rise to protists.Fungi,Plants and Animals have developed from early
protistians.
In the FIVE KINGDOM SYSTEM OF
CLASSIFICATION: -KINGDOM MONERA includes bacteria. These
organisms show extensive diversity.
(1) These are prokaryotic unicellular organisms.
(2) Cell wall is noncellulosic (polysaccharides
+amino acids)
(3) Nuclear membrane is absent.
(4) Mode of nutrition is autotrophic (chemosynthetic
and photosynthetic) and Heterotrophic (saprophytic and parasitic)
A7
Students we know that all living organisms are
classified into five kingdoms:-
1 Monera
2 Protista
3 Fungi
4 Plantae
5 Animalia.
Today we will discuss Kingdom Monera in detail. It includes all the prokaryotic unicellular organisms. Prokaryotic organisms are those which lack nuclear membranes i.e. DNA is naked. Genetic material is not organised in nucleus. DNA is coiled and is called nucleoid. Membrane bound organelles are absent.BACTERIA are the sole members of Kingdom Monera.
OCCURRENCE OF BACTERIA.It is found everywhere i.e in soil, air, water, hot springs, deserts, snow, deep oceans,
on and inside other organisms.
SHAPES OF BACTERIA.
2 BACILLUS - These are rod shaped bacteria.
3 VIBRIO - These are comma shaped bacteria.
4 SPIRILLUM - These are spiral shaped bacteria.
1 AUTOTROPHIC:
These bacteria synthesise their own food from inorganic
substrates. Bacteria that uses radiant energy to
prepare their food are called PHOTOSYNTHETIC AUTOTROPHS. Bacteria that
synthesise food from inorganic raw materials with the help of energy released
from inorganic chemical reactions are called CHEMOAUTOTROPHIC bacteria.
2 HETEROTROPHIC:
These bacteria depend on other organisms or on dead
organic matter for food.
REPRODUCTION IN BACTERIA
Reproduction in bacteria takes place by following
methods: -
A. Fission
B. Forming spores
C. Sort of sexual reproduction by primitive type of
DNA transfers from one bacterium to other.
MAJOR GROUPS OF MONERA ARE
1. Archaebacteria
2. Eubacteria.
1. ARCHAEBACTERIA:
They are the oldest form of life. Their cell wall
structure is different and this helps them to survive in most harsh habitats.
HALOPHILES: These can live in extremely salty areas
THERMOACIDOPHILES: These can live in hot springs.
METHANOGENS: These can live in marshy areas. These
are present in gut of ruminants (cows and buffaloes) and are responsible for
methane (biogas) production from the dung.
2. EUBACTERIA
There are thousands of true bacteria. They have
rigid cell wall and if they are motile
then they have flagellum.
1) Cyanobacteria: It is also called blue green algae. It has chlorophyll a. These are PHOTOSYNTHETIC AUTOTROPHS. It may be unicellular, colonial or filamentous,fresh water/marine or terrestrial. Mucilaginous sheath surrounds the colonies. Some of these organisms have specialised cells that fixes atmospheric nitrogen. These cells are called heterocysts, e.g Nostoc and Anabaena.
2) Chemosynthetic
autotrophic bacteria helps in recycling of nitrogen,
phosphorous, iron and sulphur.
3) Heterotrophic
bacteria are most abundant. Majority of them are
decomposers. These bacteria helps in forming curd
from milk, antibiotics formation,fixing nitrogen in legume roots. Some bacteria
causes diseases in humans, crops,farm animals and pets.
4) Mycoplasma are groups of monerans that lack cell
wall. They are smallest living cells. They can survive without oxygen.
LET US KNOW, WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
(a) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:--
Q1. Round or
spherical shaped bacteria is called
(A) Coccus.
(B) Bacillus §
(C) Vibrio.
(D) Spirillum
Q2. Blue green
algae is also called
(A) Cyanobacteria
(B) Eubacteria
(C) Both of these.
D) None of
these.
Q3. Bacteria that
lives in extremely salty areas are called
(A) Thermoacidophiles.
(B) Halophiles
(C) Methanogens.
(D None of these
Q4.
Cyanobacterial cells which are specialised for nitrogen fixation are
(A) Phycobilisomes
(B)Heterocyst
(C) Hormogonia.
(D) Trichomes
Q5. The bacterial
genome is called
(A) Nucleus
(B) Nucleolus
(C) Nucleoid
(D) None of these
(b) TRUE / FALSE
Q1. Prokaryotic cells lacks nuclear membrane.
Q2. Heterotrophic bacteria can produce their own
food.
Q3. Virus is responsible for citrus canker disease.
(c ) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
Q1. ---—--are the sole members of Kingdom Monera
Q2. -—---- are the smallest living cells.
ANSWER KEY
(a) - MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Ans 1. (A) Coccus. (Bacillus bacteria is rod shaped)
Ans 2. (A) Cyanobacteria (These are photosynthetic
autotrophs)
Ans 3. (B) Halophiles (These can tolerate high salt
concentration)
Ans 4. (B) Heterocysts (These are thick walled
cells)
Ans 5. (C) Nucleoid (Genetic material is in direct
contact with cytoplasm)
(b) - TRUE/ FALSE
Ans 1. True
Ans 2. False. (Autotrophic bacteria can produce the
own food)
Ans 3. False. (Bacteria are responsible for citrus
canker)
(c)- FILLIN THE BLANKS
Ans 1. Bacteria.
Ans 2. Mycoplasma. (These can survive without
oxygen)
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q1. Give difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic
bacteria.
Q2. Write a note on archaebacteria.
Q3. Give characteristics of Kingdom monera.
A8
There are five kingdoms in which all the living
organisms are placed.
1. Kingdom Monera
2. Kingdom Protista
3. Kingdom Fungi
4. Kingdom Plantae
5. Kingdom Animalia
We will discuss here Kingdom Protista in detail:--
All single-celled eukaryotes are placed under
kingdom Protista. For our convenience, Kingdom Protista is divided into
Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates,Euglenoids, Slime moulds and Protozoans.
(Note: - Out of these five we are discussing first
two groups here.)
Members of Protista are primarily aquatic. This
Kingdom forms a link with the others,dealing with plants, animals and fungi.
Being eukaryotes, the protistan cell body contains a well-defined nucleus and
other membrane-bound organelles. Some have flagella or cilia. Protists
reproduce asexually and sexually by a process involving cell
fusion and zygote formation.
1.CHRYSOPHYTES
This group includes diatoms and golden algae
(Desmids). They are found in freshwater as well as in marine environments. They
are microscopic and float passively in water currents (Plankton).Most of them
are photosynthetic. In diatoms the cell wall form two thin overlapping shells,
which fit together as in a soap box.The walls are made up of silica and their
deposition and accumulation over billions of years is referred to as
Diatomaceous Earth.
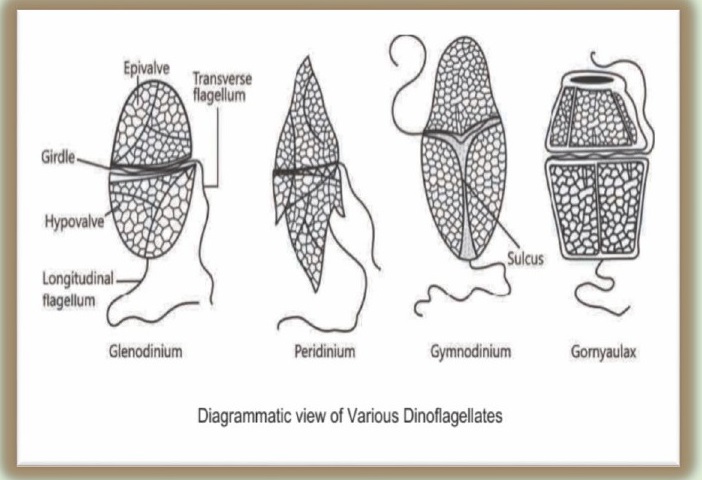
2. DINOFLAGELLATES
These organisms are mostly marine and
photosynthetic. They appear yellow,green, brown, blue or red depending on the
main pigments present in their cells.The cell wall has stiff cellulose plates
on the outer surface. Most of them have two flagella; one lies longitudinally
and the other transversely in a furrow between the wall plates. Very often red
dinoflagellates (like Gonyaulax) undergo rapid-
-multiplication that they make the sea appear red
(Red Tides). Toxins released by such large numbers may even kill other marine
animals such as fishes.
LET US KNOW, WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
a) MCQs.:-
Q1. Unicellular
eukaryotic organisms are placed in :
(a) Kingdom Animalia
(b) Kingdom Plantae
(c) Kingdom Protista
(d) Kingdom Monera
Q2. Which of the
following group not belongs to Kingdom Protista-?
(a) Slime moulds
(b) Protozoans
(c) Archaebacteria
(d) Chrysophytes
Q3. In the Five
Kingdom system of Whittaker, how many kingdoms are eukaryotes —
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d)5
Q4. Toxins
released by these can kill other marine animals like -
(a) Diatoms
(b) Golden algae
(c) Dinoflagellates
(d) Slime moulds
Q5. How many
flagella are present in dinoflagellates -
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
(b) FILL UPS.:--
Q1. and golden algae are included in Chrysophytes.
Q2. are responsible for red tides.
(c) TRUE / FALSE:--
Q1. Cell Walls of diatoms form to thin overlapping
cells like a soap box.
Q2. Most of the members of Kingdom Protista are
terrestrial.
Q3. All Protozoans are autotrophs.
ANSWER KEY (PART-A)
a) MCQs.:—
Ans 1. (c) Kingdom Protista (Protists are
Unicellular and have well defined nucleus. )
Ans 2. (c). Archaebacteria (Archaebacteria belongs
to Monera.)
Ans 3. (c). 4 (Protista, Fungi, plantae and Animalia
are Eukaryotes. )
Ans 4. (c). Dinoglagellates (On rapid multiplication
they produce large toxins. )
Ans 5. (b). 2 (Dinoflagellates have two flagella.)
(b) FILL UPS.:-~
Ans 1. Diatoms
Ans 2. Gonyaulax
(c) TRUE / FALSE:~
Ans 1. TRUE
Ans 2. FALSE (Most of the members of Kingdom
Protista are Aquatic.)
Ans 3. FALSE (Protozoans are heterotrophs. )
PART-B: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. What do you mean by diatomaceous earth?
Q2. What is the nature of cell wall in diatoms?
Q3. Write a short note on Dinoflagellates.
A9
Kingdom Protista,includes all single celled,
eukaryotes.(having true membrane bound nucleus & other organelles and DNA
wrapped in Histone proteins.)(Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Slime
moulds and Protozoans).The first tvo groups have been discussed in assignment
no.08. Now, we are discussing last three groups here.
1. EUGLENOIDS
Majority of them are freshwater organisms found in
stagnant water. Instead of a cell wall they have a protein rich layer called
pellicle, which makes their body flexible. They are photosynthetic in the
presence of sunlight, when deprived of sunlight they behave like
heterotrophs by predating on other smaller
organisms.Interestingly the pigments of euglenoids are identical to those
present in higher plants. Example:- Euglena.
2. SLIME MOULDS
Slime moulds are saprophytic protists. The body
moves along decaying twigs and leaves engulfing organic material. Under
suitable conditions they form an aggregation called plasmodium, which may grow
and spread over several feet. During unfavourable conditions the plasmodium
differentiates ! and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores at their tips.These
spores possess tough walls. They are extremely resistant and survive for many
years,even under adverse conditions. The spores are dispersed by air currents.
3. PROTOZOANS
All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as
predators or parasites. They are believed to be primitive relatives of animals.
There are four major groups of protozoans,according to mode of locomotion:
(a) Amoeboid protozoans : These organisms live in freshwater, sea water or moist soil. They move and capture their prey by putting out pseudopodia. as in amoeba. Marine forms have silica shells on their surface.Some of them such as entamoeba are parasites.
(b) Flagellated protozoans: The members of this
group are either free living or parasitic. They have flagella. The parasitic
forms causes diseases such as sleeping sickness. Example; Trypanosoma gambiens.
Example:- Paramecium.
(d) Sporozoans: This includes diverse parasitic organisms,having no organs for locomotion,and have an infectious sporophytic stage in their life cycle. The most notorious is plasmodium (Malarial parasite) which causes malaria, a disease which has a staggering effect on human population.
LET US KNOW, WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
(a) MCQs.:--
Q1. Protozoans
are believed to be primitive relatives of —
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Algae
(d) Animals
Q2. Movments of
cilia brings food towards gullet in-
(a) Amoeba
(b) Euglena
(c) Paramecium
(d) Slime moulds
Q3. Naked
cytoplasm, multinucleated and saprophytic are the characteristics of -
(a) Monera
(b) Protista
(c) Fungi
(d) Slime moulds
Q4. These
unicellular eukaryotes are photosynthetic in the presence of sunlight -
(a) Protozoans
(b) Euglenoids
(c)Diatoms
(d) Dinoflagellates
Q5. These form
spores during unfavourable conditions -
(a) Dinoflagellates
(b)Protista
(c) Euglenoids
(d) Slime moulds
(b) FILL UPS:--
Q1. A protein rich layer which make euglenoids
flexible is .
Q2. Amobea moves with the help of .
(c) TRUE / FALSE:-
Q1. Paramecium moves with the help of flagela.
Q2. Plasmodium causes malaria in humans.
Q3. Flagellated protozoans are either free living or
parasitic.
ANSWER KEY- PART (A)
(a) MCQs.:--
Ans 1. (d). Animals
Ans 2. (c). Paramecium
Ans 3. (d). Slime moulds (Slime moulds lacks cell
wall and secretes slime.)
Ans 4. (b). Euglenoids ( contain photosynthetic
pigments. )
Ans 5. (d). Slime moulds
(b) FILL UPS:--
Ans 1. Pellicle
Ans 2. Pseudopodia
(c) TRUE / FALSE:--
Ans 1. FALSE (Most of the members of Kingdom
Protista are Aquatic.)
Ans 2. TRUE
Ans 3. TRUE
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q1. How slime moulds surpass unfavourable
conditions?
Q2. How amoeba obtain their food?
Q3. Write a short note on ciliated protozoans.
A10
INTRODUCTION:
¢ Most of the fungi are multicellular eukaryotic
organisms except
yeast(unicellular).¢ Fungi are non-vascular,
non-motile organisms.
“ Cell wall is made up of chitin.“« They have no
pigments like chlorophyll, so they are not photosynthetic.
“ Most of the fungi are saprophytic (decomposers).
“ Digestion is extracellular.
“ Lack true roots,stems and leaves.
“ Fungi are more related to animals than plant
kingdom.
“ Some are parasitic; very few are symbiotic.
“ Body of fungi have thread like structures called
hyphae.
“* Hyphae are of two types: Septate and Aseptate.
« ASEPTATE FUNGI(PHYCOMYCETES):
> Mastigomycetes:
m They produce flagellated cells.
m Asexual reproduction occurs by formation of
spores.
= Gametes are usually non-flagellate.
m Sexual reproduction by gametangial contact.
mw They look multinucleate(coenocytic).
ws Examples : Albugo , Phytophthora.
> Zygomycetes:
mw They are found in freshwater and marine water.
= Most zygomycetes live on decaying plants and
animal matter.
mw They are non flagellate fungi.
mw They look multinucleate (coenocytic).
mw Asexual reproduction is by means of spores
produced in sporangia borne on thehyphae.
mw Sexual reproduction occurs by means of
conjugation tube.
ms A Zygote like structure is formed after
conjugation.
mw They bear rhizoids which act as roots.
ms Example: Rhizopus stolonifer (bread mold)—which
is used for
commercialproduction of fumaric acid.
= Asexual reproduction in Zygomycetes:
Sexual reproduction in zygomycetes:
It occurs by
conjugation.lIsogamous hyphae forms zygote.
Spores are
formed in zygote. Spores grow into hyphae.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A. Very short answer type questions:
A.) MCQ'’s:
Q1. Aseptate
fungi are of following types:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
Q2.Rhizopus(bread
mold) is an example of which fungi:
a. Mastigomycetes
b. Zygomycetes
c. Ascomycetes
d. Basidiomycetes
Q3.Lower fungi
are:
a. Multinucleate
b. Uninucleated
c. Binucleated
d. Non- nucleated
Q4.Root like
structures of fungi are known as:
a. Hyphae
b. Rhizoids
c. Sporangiospore
d. Septa
Q5.Mode of
nutrition of fungi is :
a. Autotroph
b. Heterotroph
c. Saprophyte
d. Parasitic
B.) Fill Ups:
1. Cell wallismade up of__.
2. Thread like body of fungi is known as_.
3. Hyphae are of two types and
C.)True/False:
1. Mastigomycetes are flagellated members of
aseptate fungi.
2. During asexual reproduction of zygomycetes, they
form spores.
3. Fungi have true roots,stem and leaves.
B.Short answer type questions:
1. Draw flow chart of aseptate division of fungi.
2. Write a note on sexual reproduction of
zygomycetes.
3. Write common characters of Kingdom
Fungi(eumycetes).
Answer Key
Part A:
a.) MCQ’s:
1. B (Aseptate fungi are of two types:
mastigomycetes and zygomycetes)
2. B (Rhizopus is an example of zygomycetes)
3. A (Lower fungi appears multinucleated because septae
are absent)
4. B (Root like structures of fungi are known as
rhizoids)
5. C (Fungi have saprophytic mode of nutrition)
b.) Fill ups:
1. Chitin
2. Hyphae
3. Septate and aseptate.
c.)True or False:
1. True
2. True
3. False (they lack roots stems and leaves)
A11
SEPTATE FUNGI:
It can be
unicellular(yeast) or multicellular(penicillium).
“ Hyphae are divided into cellular compartments by
walls called septae.
It consists of three subtypes :
Ascomycetes
Basidiomycetes
Deuteromycetes
1. Ascomycetes:
It's also known as sac fungi.
It's the largest phylum of fungi.Sexual reproduction takes place by Ascus (ascospores).
Ascus develops from a zygote, 2N vegetative
cell or ascogenous hyphae.Cell wall is formed of chitin.Sexual reproduction
occurs by gametangial fusion.“« Ascomycetes can be filamentous or
unicellular.Fungi with spores produced inside a sac called ascus.
Some ascomycetes are plant pathogens.Ascomycetes
make symbiotic relation with algae to form lichens. Asexual reproduction by
fission and budding. Some are edible such as Morels and Truffles which are rich
in proteins and vitamins. Some are used in food production,such as yeast is
used to produce alcohol and make bread. Penicillium species is used in
production of citric acid,oxalic acid,fumaric acid
etc. Yeast is also used in genetic research also.
Penicillium is used in production of antibiotics.
Yeast:
Yeast is a unicellular fungus used for fermentation
and for baking.
Cell wall is made up of Chitin, Phosphoric
acid,Glycogen.
Big central vacuole is present.Saprophytic mode of
nutrition.
Secrete enzyme Zymase to digest carbohydrates and
forms simple
sugars.Asexual reproduction in yeast occurs by
budding and fission.
Budding:
Fission:
Cell of yeast elongates.Nuclei divides into two nuclei. Plate formation separates cells. Each daughter cell grows separately.
(Note:
Halobial yeast : Yeast which shows asexual reproduction
by budding and fission method). Sexual Reproduction
in Yeast: occurs via Hologamy .
2. Basidiomycetes: Basidiomycetes are also known as club fungi.
They are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae.
Basidiomycetes reproduce sexually by the formation of club shaped cells called
Basidia. Basidia bear external meiospores, known as basidiospores.
Sexual reproduction also occurs by clump connection
in few
basidiomycetes, it helps in mating of hyphae of
different sexual types.Clamp connection creates genetic variation within the
hyphae.
Basidiomycetes are uninucleate when they are in the
form of
primary hyphae. Basidiomycetes are binucleate in the form of secondary hyphae(Dikaryotic hyphae).
Asexual reproduction takes place
by :
Spore formationFragmentation of mycelium (hyphae).
Chlamydospore:- it is a thick walled large resting
spore which
survives in unfavourable conditions ,such as dry or hot
seasons.
Chlamydospore germinates in favourable conditions,
it is result of
asexual reproduction. Eg. Mushrooms, Smuts, Rusts ,
Cryptococcus etc.
Sexual reproduction completed in three steps:-
1)Plasmogamy
2)Karyogamy
3) Meiosis
3.Deuteromycetes : (Fungi imperfecti)
Deuteromycetes are also known as imperfect fungi. No
sexual form of reproduction. Only asexual reproduction occurs by the formation
of spores(conidia or oidia),known as sporogenesis. Eg. helminthosporium oryzae
(causes disease brown spot on leaf in rice)( Note:it is a causal agent of the
Bengal famine of 1943. It is considered a Biological weapon used by the US
against Japan in world war 2).
Eg. Gibberella fujikuroi It is used as growth
hormone accelerating plant growth.
Special Note:Neurospora :
This fungi belongs to the Ascomycetes group of
septate fungi.tis also Known as Drosophila of the plant kingdom.Phycomycetes:
Eg. Phytophthora infestans : An oomycete or water
mold,
a fungus like microorganism that causes the serious
potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight.
USES OF FUNGI:
Fungi play an important role in yielding antibiotics
like
Penicillium. Fungi plays an important role in baking
(bread)and brewing (alcohol) eg. Yeast. Organic acids like Citric acid,Oxalic
acid and fumaric acid are produced by fermentation.Fungus Aspergilius niger is
used for it at commercial level.The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used as a
supplement in diet to increase protein value.
Some no. of molds and yeast are used to synthesise
Ergosterol which contains vitamin D. Some species of fungi are edible like
mushrooms ,dingri,truffles etc.
Lichens:
Algae + Fungi — Lichen.
It is a symbiotic partnership of algae and
fungi.Dominant partner is fungus.They are good environmental indicators(pollution
indicator of SO. Fungal partner is known as mycobiont (absorbs nutrients).
Algal partner is known as phycobiont (synthesis of
food).Mycorrhiza :
Roots of higher plant + fungus — Mycorrhiza. It's a
symbiotic relationship between the roots of higher plants and fungus. They
increase the surface area associated with plant roots ,which
increases the intake of nutrients and water from
soil.
A.) Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. MCQ's:
Q1.Sexual
reproductive structures of ascomycetes are:
a. Basidium
b. Ascus
c. Spores
d. Hyphae
Q2.In Lichens,
Fungus make symbiotic relationship with:
a. Algae
b. Roots of higher plants
c. Bryophytes
d. Yeast
Q3.Basidiomycetes
are also known as:
a. Club fungi
b. Sac fungi
c. Lichens
d. Fungi imperfecti
Q4.Dikaryotic
Hyphae has no. of nuclei:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
Q5. Which fungus
is used as growth hormone in plants:
a. Gibberella fujikuroi
b. Rhizopus
c. Albugo
d. Agaricus
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a good source of .
2. Roots of higher plants + Fungus— .
3. are good environmental indicators.
3.True/False:
1. Yeast is a multicellular fungus.
2. Aspergillus niger is used to form organic acids.
3. Mycorrhizae increases the fertility of soil.
B.)Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Write a short note on asexual reproduction of
yeast.
2. Show different types of septate fungi with the
help of flow chart.
3. Write uses of fungi.
Answer Key
1. MCQ’s:
1.a (Sexual reproductive structures of ascomycetes
are called ascus)
2.a (Fungi and algae make symbiotic relationship to
form lichens)
3.b (Basidiomycetes are also known as Club fungi)
4.b (Dikaryotic hyphae have two nuclei)
5.a (Gibberella fujikuroi is used as a growth
hormone in plants because it produces gibberellin)
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. Protein
2. Mycorrhizae
3. Lichens
3. True/False:
1. False (Yeast is a unicellular fungus)
2. True
3.True
A12
INTRODUCTION:Viruses,
viroid, prions and lichen are not mentioned in 5-kingdom system of
classification by R.H. Whittaker, because they are acellular and not truly
living.
VIRUS:Virus
is a microscopic, infectious particle that can reproduce or replicate within
the living cell of an organism or host. Viruses cannot reproduce without a host
cell. They infect almost all living forms such as animals,plants, and
bacteria.In 1898, a Dutch scientist, Martinus Beijerinck discovered the world’s
first virus which was the tobacco mosaic virus. He conducted an experiment to
show that there is another infectious particle that is smaller than bacteria
and responsible for the infection in tobacco plants.In 1892, Dmitri lvanovsky
discovered Virus.
Characteristics of viruses:
1. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites.
2. They are non-cellular.
3. They are on the borderline between living nor
non-living.
4. They are parasitic
5. They are microscopic.
6. They are infectious (The genetic material in them
is infectious)
7. They require a host. (obligate parasites)
8. They don’t have a metabolism.
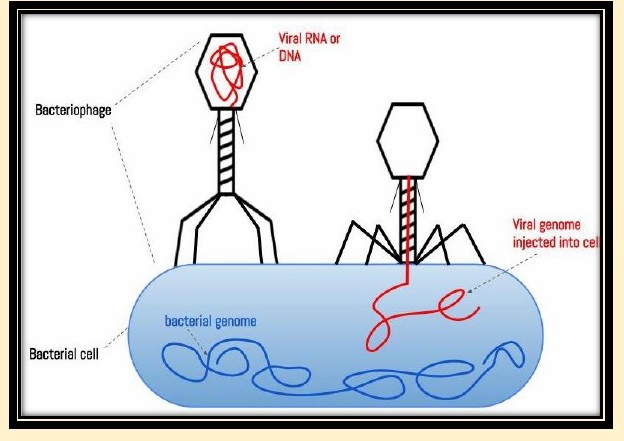
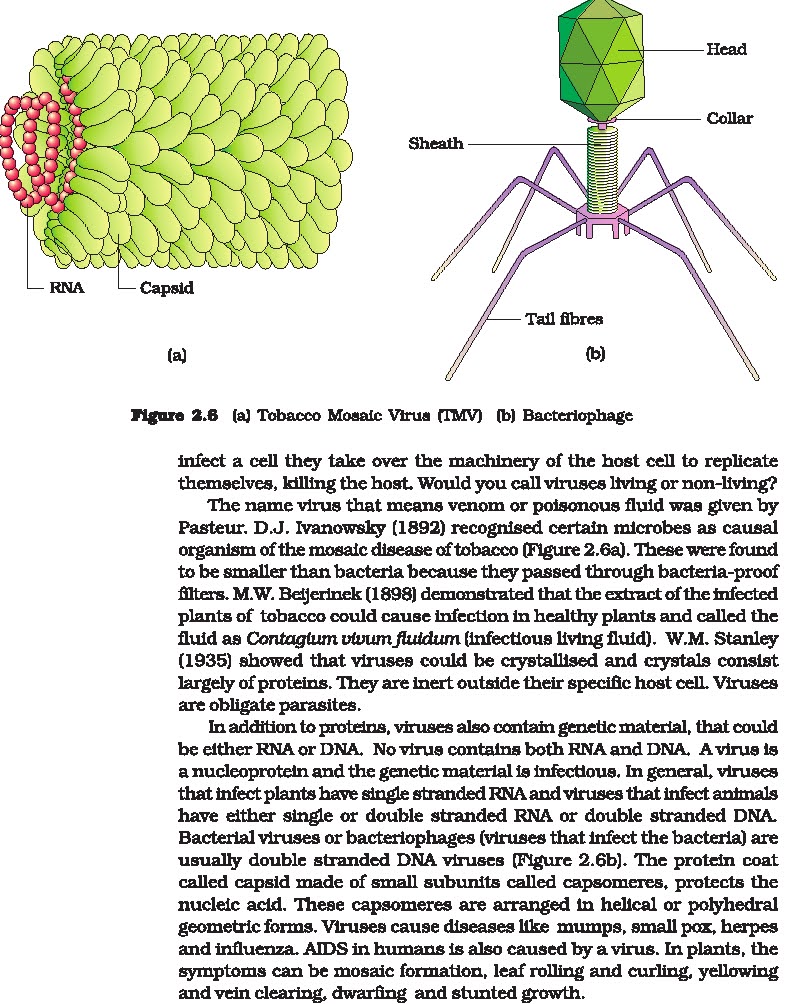
Structure of a Virus:Viruses
can replicate only inside a living cell. Therefore, it contains only those
parts needed to invade and control a host cell.Viruses vary in their individual
structure, but all viruses contain two structures.
1. Nucleic acid:
DNA “or” RNA (never both)
2. Capsid:
protein coat. The protein coat consists of smaller subunits called capsomeres.
3. Envelope: made of lipid.
Envelopes are found only in some viruses.
4. Tail: viruses that infect
bacteria have a tail which is used for attachment.
Viruses are borderline organisms between living and non living
Viruses can reproduce inside a host just like any
other living
organisms, but this ability to reproduce is lost
once virus is outside
the host cell. This is because viruses are
acellular, they don’t have
a cellular machinery of their own. Also, viruses can
be crystallized,
which is a property of non-living things.
viral replication:
viruses hijack host cell machinery to reproduce;
Viruses are noncellular and cannot reproduce on
their own. Both
enveloped and non-enveloped viruses use their
protein coat to
enter attack a host cell and deposit their genetic
material inside
host cell. They then hijack host cells machinery to
make their own
copies and hence reproduce.
Virion: It is the “extracellular” infectious form. It must have an envelope and membrane proteins in addition to nucleic acid and capsid.
Consists of nucleic acid and Complete infective form of a protein coat virus: contains envelope as well Priucont (conte mn al
Bacteriophage:Bacteriophage was discovered
independently by Federick Twort and Felix d’Herelle independently in 1915 and
1917 respectively. They are viruses that infect bacteria.
VIROIDS:Viroids are low molecular weight infectious agents with no protein coat and have a low molecular weight RNA as shown in the picture.In 1971, a plant pathologist named Theodor Otto Diener first discovered the Viroids. He found an acellular particle when he was working in an Agriculture Research Service and named this particle as viroid, meaning “virus-like.” At present-33 species of viroid have been identified.
LICHENS:Lichens are a symbiotic association in which algae and fungi live together. Algal component is called a phycobiont and fungal component is called a mycobiont.Algae being autotrophic, prepare food for fungus. Fungi provide shelter and absorb mineral nutrients and water for its partner.
2. The protein coat of viruses that enclose the genetic material is called
(a) Virion
(b) Capsid
(c) Peplomers
(d) Capsomers
3. Which of the
following statements are true about a virion?
(a) Lytic phage
(b) Lysogenic phage
(c) The viral capsid
(d) An infectious and fully formed viral particle
4. Which of the
following is the genome of the virus?
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) DNA or RNA
(d) DNA and RNA
5. The viral
envelope is made of ............?
(a) Proteins
(b) Glycoproteins
(c) Lipids
(d) All of the above
b) TRUE/FALSE:
1. Viroids do not have a protein coat.
2. Viruses are obligate parasites.
3. Lichen is a symbiotic association between plants
and fungi.
4. AVirus can have both DNA and RNA
c) FILL UPS:
1. Algal component of a lichen is called......
2. Corona virus official name by ICTV is .......
3. ICTV full form is......
4. National Institute of virology isin ....
ANSWER KEY - PART-A
a) Multiple choice questions:
1. (a) Protein coat and nucleic acid.
2. (b) Capsid.
3. (d) An infectious and fully formed viral particle
(Virion is extracellular infectious form having additional components as well:
envelope and membrane proteins)
4. (c) DNA or RNA (A virus can never have both).
5. (d) All of the above (Envelope has all three
components).
b) True/false:
1. True.
2. True. They can reproduce only when inside a host.
3. False. It's an association between fungus and an
Algae.
4. False. A Virus can never have both DNA and RNA
together.
c) Fill ups:
1. Phycobiont.
2. SARS-CoV-2.
3. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
4. Pune. (India’s second virology institute is
proposed to be set up in Mohali. At present India has only one virology
institute)
Part-B-- SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Ques 1: Label the parts of virus given in following
diagram.
Ques 2: Are viruses living or non-living? Comment.
PART-C-- LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Ques 1. Give a brief account of viruses with respect
to their structure and nature of genetic material. Also name 4 common viral
diseases.
A13
R.H. Whittaker classified organisms into 5 kingdoms
on the basis of:
1. Cell structure- Eukaryotic and prokaryotic
2. Body organisation- unicellular or multicellularity
3. Mode of nutrition- Autotrophic or heterotrophic
etc.
4. Mode of reproduction- Asexual or sexual
To appreciate the uniqueness of organisms classified
under the 5-kingdom classification, study of differences is must.Hence in this
daily dose, we would look at comparisons and differences between
or among different forms.
ORGANISMS:
NUTRITION:
KINGDOM PROTISTA:Kingdom
Protista is further divided on the basis of mode of nutrition,morphology, cell
wal! structure etc.
LICHEN:It's
unique because it's a symbiotic association between 2- different types of organisms-
Fungi (Mycobiont) and an Alga (Phycobiont)
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
a) Multiple choice questions:
1. Which of the
following can be found in extremely saline conditions:
(a) Mycobacteria
(b) cyanobacteria
(c) Archaebacteria
(d) Eubacteria
2. Which of the
following statements is false about fungi?
(a) eukaryotic
(b) autotrophic
(c) cell wall made of chitin
(d) none of these
3. Which of the
following statements are true about protists?
(a) unicellular mostly
(b) eukaryotic
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
4. Cell wall in
bacteria is made up of:
(a) cellulose
(b) fungal cellulose
(c) chitin
(d) peptidoglycan
5. Blue green
algae belong to:
(a) protista
(b) prokaryotes
(c) fungi
(d) archaebacteria
b) Eill ups:
1. ....... have siliceous deposits in their cell
wall.
2. Proteinaceous covering called pellicle is present
in......
3. Asexual spores don't form in .............
subdivision of fungi.
4. Animals store reserve food in the form
of.............
c) Irue/false:
1. Archaebacteria are the modern bacteria, most
evolved ones.
2. Dinoflagellates have 2 flagella.
3. Mushrooms belong to basidiomycetes division of
fungi.
4. Fungi are multicellular, eukaryotic and
heterotrophic organisms.
5. Animal cells have a cell wall made of a soft
material which makes their body flexible.
a) Multiple choice questions:
1. (c) Archaebacteria: They are primitive bacteria
which can survive in extreme conditions
2. (b) autotrophic: fungi are heterotrophic as they
lack chlorophyll
3. (c) both (a) and (b): protists are mostly
unicellular eukaryotes
4. (d) peptidoglycan: cell wail in bacteria is made
of peptidoglycan
5. (b) prokaryotes: Blue green algae or cyanobacteria
are prokaryotic.
b) Fill ups:
1. Chrysophytes
2. Euglena
3. Basidiomycetes
4. glycogen
c) True/false:
1. False: Archaebacteria, the most primitive and
least evolved forms of bacteria
2. True: They have 2 flagella- one short and one
long.
3. True: Mushrooms (Agaricus) belong to
basidiomycete fungi.
4. True
5. False: Cell wall is absent in kingdom Animalia.
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Write major differences between kingdom Monera
and kingdom Protista.
2. Differentiate between mycobiont and phycobiont.
3. Compare Chrysophytes with Dinofllagelates.
PART-C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Differentiate the characteristic of various
subdivisions of fungi under
(a) mode of nutrition
(b) mode of reproduction.
A14
INTRODUCTION
Classification, in biology, is the establishment of
a hierarchical system of categories on the basis of presumed natural
relationships among organisms.
Taxonomy: The science of biological classification,
that deals with
IDENTIFICATION, NOMENCLATURE AND CLASSIFICATION,is
commonly called taxonomy.
IMPORTANCE OF CLASSIFICATION:
thelps in the identification of living organisms as well as in understanding
the diversity of living organisms. To understand and study the features,
similarities and differences between different living organisms and how they
are grouped under different categories.
Father of Classification:Carolus Linnaeus is known
as father of classification. He was the Swedish botanical taxonomist. He
introduced two kingdom system, Kingdom Plantae and Animalia.Carolus Linnaeus
was the first person to formulate and adhere to a uniform system for defining
and naming the world's plants and animals Objectives of Classification:To
arrange the species in various categories on the basis of their similarities
and dissimilarities.
To evolve a truly natural or phylogenetic system
which should indicate
origin and evolution of the species. - Helping in
easy identification of organisms.
The main objectives of taxonomy:Obtaining a suitable
specimen .(collecting, preserving and, when necessary,making special
preparations). Comparing the specimen with the known range of variation of
living things.Correctly identifying the specimen if it has been described, or
preparing a description.
AIMS OF CLASSIFICATION:Due to classification, there is no need to study each and everythingabout all the living organisms.Classification provides a picture of plants and animals. Classification gives an idea of similarities and differences between various groups example, vertebrates and invertebrates.
N.C.E.R.T. EXERCISE SOLUTIONS: (Qs.1 to 6)
1. Discuss how
classification systems have undergone several changes over a period of time?
Ans. Linnaeus proposed a two kingdom system of
classification with Plantae and Animalia kingdoms was developed that included
all plants and animals respectively.It became very difficult to group some
living things into one or the other, so early in the past century the two
kingdoms were expanded into five kingdoms:Protista (the single-celled
eukaryotes); Fungi (fungus and related organisms);Plantae (the plants);
Animalia (the animals); Monera (the prokaryotes).
2. State two
economically important uses of :
(a)Heterotrophic Bacteria (b) Archaebacteria.
Ans. (a) Economically important uses of
Heterotrophic Bacteria:
1. Many bacteria like Lactobacillus helps in the
production of curd from milk.
2. They act as decomposers and help in the formation
of humus e.g.
Pseudomonas.
3. Many antibiotics are obtained from some species
of bacteria like
streptomyces, Bacillus etc.
(b) Economically important uses of Archaebacteria:
1. Since the enzymes from these organisms can
survive harsh conditions
they have many industrial applications in
biotechnology
2. Many of the thermostable enzymes used in the
manipulation of DNA are derived from Archaebacteria.
3. Methanogens of the Archaebacteria are mainly
involved in the biogas
production.
3. What is the
nature of cell walls in diatoms?
Ans. The cell walls of diatoms are made of
silica.Their cell wall construction is known as frustule.When the diatoms die,
the silica in their cell walls gets deposited in the form of diatomaceous
earth.
4. Find out what
do the term ‘Algal Bloom’ and ‘Red Tides’ signify.
Ans. (A) Algal Bloom:
(1) An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid
increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine
water systems, and is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from
their pigments.
(2) The term algae encompasses many types of aquatic
photosynthetic
organisms, both macroscopic, multicellular organisms
like sea weed and
microscopic, unicellular organisms like
cyanobacteria.
(3) An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest.
(B) Red Tides:Red tides are a phenomenon of discoloration of sea surface. Itis a common name for harmful algal blooms occurring along coastal regions, which are resulted from large concentrations of aquatic microorganisms, such as protozoans and unicellular algae (e.g. dinoflagellates and diatoms). Very often Red Dinoflagellates,
GONYAULAX, undergo rapid multiplication to make the
sea appear Red.
6. Describe briefly the four major groups of Protozoa?
Ans. There are four major groups of Protozoa:
1. Amoeboid Protozoans: These organisms lives in
fresh water, sea water or moist soil. They move and capture their prey by
putting out pseudopodia (false feet) as in Amoeba. Marine forms have silica
shells on their surface.Some of them such as Entamoeba are parasites.
2. Flagellated Protozoans: The members of this group
are either free living or parasitic. They have flagella. The parasitic form
cause diseases such as sleeping sickness. Example: Trypanosoma.
3. Ciliated Protozoans: These are aquatic, actively moving organisms
because of the presence of thousands of cilia. They
have a cavity(gullet) that opens to the outside of the cell surface. The
coordinated movement of rows of cilia causes the water laden with food to be
steered into the gullet.Example: Paramoecium.
4 .Sporozoan Protozoans: This includes diverse
organism that have an
infectious spore like stage in their life cycle. Tne
most notorious is
Plasmodium ( Malarial Parasite) which cause Malaria,
a disease which has a staggering effect on human populations.
A15
RECAPITULATION:Robert
Whittaker is known as father of five kingdom system.Earlier Robert Whittaker
introduced only four kingdom systems in 1960, Kingdom Monera, Protista,
Animalia and Plantae.
Later on he introduced fifth Kingdom Fungi.
The animal kingdom is the largest kingdom with over
1 million known
species. All animals consist of many complex cells. They are also heterotrophs.
KINGDOM MONERA
CHARACTERSTICS:The Monerans are unicellular organisms The cell wall is rigid and made up of peptidoglycan.Asexual Reproduction through binary fission.They contain 70S ribosomes.Flagella serves as the locomotory organ.It lacks organelles like mitochondria, lysosomes, plastids, Golgi bodies,endoplasmic reticulum, centrosome, etc.
ARCHAEBACTERIA:They
are present in rumen (first part of stomach) of cattles. This is simple stand
most primitive group of bacteria. The cell wall of these bacteria is made of
polysaccharides and proteins (peptidoglycans and muramic acid are absent in
cell wall). Further branched chain lipids are present in plasma membrane of
archaebacteria, due to which these can face extremes of conditions of
temperature and pH. Archaebacteria are considered to be ‘oldest of living
fossils’. Three main groups of archaebacteria are following Methanogens,
Halophiles and Thermoacidophiles
EUBACTERIA:Eubacteria are known as true bacteria, and are cauterized by the presence of a rigid cell wall, and if motile, a flagellum.
The cyanobacteria or blue-green algae have
chlorophyll a similar to green plants and are photosynthetic autotrophs.They
are unicellular, prokaryotic microscopic cells.Their cell membrane contain
lipids made up of glycerol-ester lipids.Chromosome is circular and nucleosomes
maybe present.The cell wall is made up of Peptidoglycan (Murein).
KINGDOM PROTISTA
CHARACTERSTICS:All protists are
eukaryotic organisms.Most protists are aquatic, others are found in moist and
damp environments.
Most are unicellular, however, there are a few
multicellular protists such as the giant kelp.They may be autotrophic or
heterotrophic in nature.
KINGDOM FUNGI
CHARACTERSTICS:Fungi are eukaryotic, non-vascular,
non-motile and heterotrophic organisms.They may be unicellular or filamentous.
They reproduce by means of spores.Fungi exhibit the
phenomenon of alternation of generation.Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot
perform photosynthesis.Fungi store their food in the form of starch.
Biosynthesis of chitin occurs in fungi.The nuclei of
the fungi are very small.The fungi have no embryonic stage. They develop from
the spores.The mode of reproduction is sexual or asexual.Some fungi are
parasitic and can infect the host.Fungi produce a chemical called pheromone
which leads to sexual reproduction in fungi.
Examples include mushrooms, moulds, yeast.
KINGDOM PLANTAE
CHARACTERSTICS:They
are eukaryotic and multicellular.Their cells have cellulose walls.Majority have
transport system.They have photosynthesis hence autotrophic.Reproduction is
both asexual and sexual.They show alternation of generation.Some examples of
plants are trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines,ferns, mosses, and
green algae.
CHARACTERSTICS:These organisms
are multicellular, eukaryotic and without chlorophyll.The cells possess no cell
walls and plastids.
Central vacuoles are absent but small vacuoles may
occur.Most of them are free moving (except sponges and some
coelentrates)Nutrition is primarily ingestive.Reproduction is generally sexual
and the haploid stage is represented only by gametes.Growth of organisms stops
when the adult stage is reached.
EXERCISE SOLUTIONS- Il (Qs.07 to 12)
7. Plants are
autotrophic. Can you think of some plants that are partially heterotrophic?
Ans. Mostly all plants are autotrophic in nature as
they synthesize their food by photosynthesis in presence of chlorophyll, water,
carbon dioxide and sun light but also there are a few members are partially
heterotrophic in nature such as insectivorous plants or parasites. They are
unable to synthesize their food by photosynthesis due to lack of chlorophyll
pigment. Bladderwort and Venus fly trap are examples of insectivorous plants
and Cuscuta is parasites.
8. What do the
terms Phycobiont and Mycobionts. Signify
Ans. Phycobiont and Mycobionts:
1. Phycobiont refers to the algal component of the
lichens.
2. Mycobiont refers to the fungal component of the
lichens.
3. Both of these are present in a symbiotic
relationship in which algae prepare food for fungi due to the presence of
chlorophyll whereas the fungus provides shelter to algae and absorbs water and
nutrients from the soil.
9. Give a
comparative account of the classes of Kingdom Fungi under the following:
(i) Mode of Nutrition.
(ii) Mode of reproduction.
10. What are the
characterstic features of Euglenoids?
Ans. Characterstic features of Euglenoids:
1. Euglenoids (such as Euglena) are unicellular
protists commonly found in fresh water.
2. Instead of cell wall, a protein-rich cell
membrane known as pellicle is present.
3. They bear two flagella on the anterior end of the
body.
4.A small light sensitive eye spot is present.
11. Give a brief
account of viruses with respect to their structure
and nature of genetic material. Also name four
common viral
disease.
Ans:
1. Viruses are sub-microscopic infectious agents
that can infect all living organisms.
2. A virus consists of genetic material surrounded
by a protein coat
3.The genetic material may be present in the form of
DNA or RNA.
4.Most of the viruses, infecting plants, have single
stranded RNA as genetic material.
5. On the other hand, the viruses infecting animals
have single or double stranded RNA or double stranded DNA.
6. Bacteriophages or viruses infecting bacteria
mostly have double stranded DNA.
7. Their protein coat called capsid is made up of
capsomere subunits.
8. These capsomeres are arranged in helical or
polyhedral geometric forms.A.|.D.S, small pox, mumps, and influenza are some
common examples of viral diseases.
12. Organize a
discussion in your class on the topic - are viruses living or non-living?
Ans. Viruses are non-living features intermediate
between non-living and living organisms.On the basis of characters, such as
non-cellular organization, inactivity outside the host organism, lack of
respiration and cellular metabolism, these are caused non-living.
Similar to non-living objects viruses can be
crystallized and precipitated.Similar to living beings, they possess genetic
material (DNA or RNA), property of mutation, irritability, can grow and
multiply inside the host cell.They are intracellular obligate parasites and
attack specific hosts.Thus, keeping these points in mind, it is quite difficult
to ascertain whether viruses are living or non-living.
Chapter 2 Biological Classification