10- CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
CHAPTER NO.10 CELL CYCLE & DIVISON
A100
INTRODUCTION:
CELL CYCLE
- The cell cycle is a process in which a cell grows and divides to
create a copy of it. Some organism reproduce through
the cell cycle and in
complex multi cellular organism, the cell cycle is
used to allow the organism to
grow, and to replace cells as they grow worn out. In
animals, the whole cell cycle
takes around 24 hours from start to finish.
Cell cycle is ordered sequence of events that occurs
in a cell in preparation of cell division .The cell cycle is four stage
processes in which the cell increases in size,copies its DNA an: prepare to
divide .The stages Gi, S, G2 make up
interphase which accounts for the span between
successive cell divisions.
On the basis of stimulatory and inhibitory messages
a cell receives, it decides
whether it should enter the cell cycle and divide.
Cell cycle consists of two parts;
1) Interphase
2) M-phase
1. INTERPHASE
- It is the period between the end of one cell division to the
beginning of next cell division, so it is called
resting phase but actually highly
metabolically active phase in which cell prepare
itself for next cell division so
called preparatory phase.Interphase is the longest
phase, in typically human
cell out of 90 hour interphase last for 89 hour. It
is the resting phase of cell.
Resting refer to the rest from division. But the
cell in the interphase, are
metabolically active. Metabolic activities are high
in this phase. During this
phase, cells grow with MRNA and tRNA is synthesized,
the chromosomes duplicate into two chromatids. The centrioles duplicate into
two. Two centrioles are formed. The Centrosphere of centrioles microtubules
arises.These microtubules form asters.
On the basis of synthesis activities, Interphase is
divided into three sub phases;
(i) Go PHASE:-
a) It is the resting phase.
b) In these cells CYCLIN - D is in decreased
concentration.
c) Growth factors stimulation takes the Gp cells to
G; phase.
d) In this phase, cell prepares itself to the cell
division.
e) The term post-mitotic is sometime used to refer
both quiescent
and senescent cell.
(ii) Gi: PHASE:
- It is the period between mitosis and initiation of DNA
replication. It is characterized by increase in cell
size and nucleus. It
involves;
a) G stands for Gap.
b) It is also called Growth Phase.
c) Polling of amino acid for protein synthesis.
d) Polling of nucleotides for synthesis of RNA and
DNA
e) Synthesis of enzymes and energy to unzip and
synthesize DNA molecules.
f) This phase is the gap period between a mitotic
phase and S phase of cell cycle.
g) It is the longer phase in which daughter cell
grows and increase in size.
h) In this phase, 20 amino acids are formed from
which millions of proteins and enzymes are formed.
i) During this phase, concentration of CYCLIN - D
increases which results in phosphorylation and activation of necessary
transcription protein.
(iii) S- Phase - It is phase between S & M
phase.It is characterized by;
a) DNA replicates so each chromosome is formed of
two sister chromatides joined at centromere.
b) Synthesis of histones (basic proteins).
c) Phosphorylation and activating proteins and
enzymes that are involved in DNA Synthesis.
d) During this, DNA Synthesis occurs.
e) DNA molecules duplicates and all the chromosomes
have been replicated.
f) Synthesis of histone proteins occur.
g) Specific events during cell divisions such as
microtubules formation and chromatic remodeling occur in this phase.
(iv) Gz PHASE: - It involves;
a) Synthesis of spindle protein.
b) Synthesis of three types of RNA molecules.
c) Synthesis and storage of ATP molecules.
d) The G2 phase is the gap between S- phase and
Mitotic phase of a cell cycle.
e) Itis the period of rapid cell growth and protein
synthesis in which the cell ready it for mitosis.
f) The nucleus increases in volume.
g) This phase has double the number of chromosomes.
h) All the other cellular components are duplicated
for two daughter cells.
i) Cyclin complexes are active which are necessary
for cell to enter into
M-phase.
2. M-PHASE (MITOSIS) :
(i) Mitosis is the distribution of the two sets of
chromosomes into two separate and equal nuclei.
(ii) This is the division stage and during this phase
cell divides.
(iii) This phase has a short duration.
(iv) This phase has two sub-phases called
Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis. Karyokinesis refer to the division of nucleus
into two daughter nuclei which has four sub-stages;
a) Prophase
b) Metaphase
c) Anaphase
d) Telophase
(v) Cytokinesis refers to division of cytoplasm
resulting in two
daughter cells.
“LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!”
PART: A —- VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
Q1. During G:
phase of cell division:
(a) RNA and proteins are synthesized.
(b) DNA and proteins are synthesized.
(c) Cell prepare for cell division.
(d) Cell undergoes duplication.
Q2. In cell cycle
DNA replication occurs during:
(a)G1 Phase
(b)G2 Phase
(c) Metaphase
(d)S- Phase
Q3. Which of following
sequence is a correct one for a meiotic cell cycle?
(a)G1-S-G2-M-G1
(b)G1-G2-S-M-G2
(c)G2-S-G1-M-G2
(d)S-G1-G2-M-S
TRUE / FALSE:
Q1. Interphase is also called as resting phase.
Q2. Increase in cell size and nuclueus occur during
G1 phase.
Q3. In animals cell cycle takes place 72 hours from
start to finish.
FILL IN BLANKS:
Q1. G1, S and G2 are sub phases of .
Q2. Replication occurs during .
ANSEWER KEY: PART-A
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
ANS:1. (a)
ANS:2. (d)
ANS:3. (a)
TRUE OR FALSE:
ANS:1. True
ANS: 2. True
ANS:3. False
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
ANS: 1. Interphase.
ANS: 2. S — Phase
PART:B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. Define cell cycle?
Q2. Write a short note on Interphase.
Q3. Show cell cycle with the help of diagram.
PART:C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. Explain different phases of cell cycle.
A101
INTRODUCTION:MITOSIS
1. It is the cell division occurring in somatic
cells.
2. It is also called as equational division as the
number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same.
3. Mitosis is generally seen in diploid cells. It
also occurs in haploid cells of some lower plants and some social
insects.
4. It involves major reorganization of all cell
components.
5. The KARYOKINESIS (division of nucleus) in mitosis
has four stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
6. The CYTOKINESIS; (division of nucleus) of mitosis
is different in plant cell and animal cell.
MITOSIS; THE SOMATIC CELL DIVISION
KARYOKINESIS: THE DIVISION OF NUCLEUS
1. PROPHASE
It is the longest phase in mitosis. It follows the S
and G2 phases of
interface in the S and G2 phases, DNA molecules are
intertwined.Chromosomal materials are untangled and condensed to form mitotic
chromosomes. They are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together
at the centromere.Centrosomes begin to move towards opposite poles of the
cell.Each centrosome radiates out microtubules called asters. The two
asters together with spindle fibres form mitotic
apparatus.Cells at the end of the prophase do not show Golgi complexes,
endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and nuclear
envelope.
2. METAPHASE
The nuclear envelope completely disintegrates so the chromosomes
spread through the cytoplasm of the cell.
Chromosomes condensation is completed. They can be
observed and studied easily under the microscope. They will have two sister
chromatids.Chromosomes come to lie at the equator.
The plane of alignment of
the chromosomes at the metaphase is called metaphase
plate.The spindle fibres from both poles are connected to chromatids by
their kinetochores in the centromere.
3. ANAPHASE
It is the shortest phase in the mitosis.Centromere of each chromosome divides
longitudinally resulting in
the formation of two daughter chromatids
(chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei).As the spindle fibres contract the
chromatids move from the equator to the opposite poles.
4. TELOPHASE
Chromosomes cluster at opposite poles and uncoil into chromatin
fibres.Nuclear envelope develops around the
chromosome clusters at each pole. So, two daughter nuclei are formed.Nucleolus,
Golgi complex and ER reappear.The spindle fibres disappear.
CYTOKINESIS
It is the division of cytoplasm to form two daughter cells.It starts when
TELOPHASE is in progress.
CYTOKINESIS IN ANIMAL CELL:Here,
a cleavage furrow is appeared in the plasma membrane.
It gradually deepens and joins in the centre
dividing the cytoplasm
into two.CYTOKINESIS IN PLANT CELL:It is different
from cytokinesis in animal cells due to the presence of cell wall.In plant
cells, the vesicles formed from Golgi bodies accumulate at the equator. it
grows outwards and meets the lateral walls. They
fuse together to form cell-plate. It separates the
two daughter cells.
Later, the cell plate becomes the middle
lamella.During cytokinesis, organelles like mitochondria and plastids get
distributed between the daughter cells.
In some organisms, Karyokinesis is not followed by
Cytokinesis. As a result, multinucleate condition (syncytium) arises. eg.
liquid endosperm in coconut.
SIGNIFICANCE OF MITOSIS
It produces diploid daughter cells with identical genome.
It helps to retain the same chromosome number in all
somatic cells.It helps in the body growth of multicellular organisms. Mitosis
in the meristematic tissues helps in a continuous growth of plants
throughout the life.It restores the
nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio that disturbed due to cell growth.It helps in cell
repair & replacement. e.g. cells of the upper layer of the epidermis,
lining of the gut and blood cells.
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A) MCQs
1. Mitosis is
characterised by:
a. Reduction division
b. both (a) and (b)
c. Equal division
d. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
2. Cleavage
differs from mitosis in:
a. synthetic phase
b. both (a) and (b)
c. growth phase
d. none of these
3. In mitosis
centromere divides at:
a. Metaphase
b. Anaphase
c. Telophase
d. Prophase
4. During cell
division, nuclear envelope reappears in:
a. Interphase
b. Telophase
c. Prophase
d. G2 phase
5. DNA
duplication takes place in:
a. S- phase of cell cycle
b. G2 phase of cell cycle
c.G; phase of cell cycle
d. None of these
B) TRUE /FALSE
1. The cell cycle involves amitosis, mitosis and
meiosis.
2. Mitosis occurs only in multicellular organisms.
3. Anastral spindle occurs in animal cells.
C) FILL UPS
1. Somatic cells multiply by ...............
2. ............. Chromosomes are exactly alike.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
A) MCQs
Ans. 1:
In this division the chromosomes number remains same
in the daughter
cells.
Ans. 2: ¢
Cleavage differs from mitosis in growth phase. There
is no growth phase
in cleavage.
Ans. 3: b
In Anaphase stage centromere divides.
Ans. 4: b
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane reappear during
Telophase.
Ans. 5: a
DNA duplication takes place during S- phase or
synthetic phase of cell division.
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. False: The cell cycle involves INTER PHASE and
M-PHASE.
2. False: Mitosis occurs in all the somatic cells of
all the organisms.In unicellular organisms it is the source of reproduction
also.
3. False: Anastral spindle occurs in higher plants.
C) FILL UPS
1. Mitosis
2. Homologous
1. Why is mitosis known as equational division?
2. Why is so called resting stage, the interphase
considered the most
active stage of cell cycle?
3. Write a short note on spindle apparatus.
1. What is the significance of mitosis?
A102
INTRODUCTION:MEIOSIS
It is the division of diploid germ cells that
reduces the chromosome number
by half forming haploid daughter cells (gametes).It
occurs during gametogenesis.
It leads to the haploid phase in the life cycle of
sexually reproducing
organisms.Fertilisation restores diploid phase.
KEY FEATURES
OF MEIOSIS:It involves two cycles (meiosis | and meiosis Il)
but only a single cycle of DNA replication.
It involves pairing of homologous chromosomes and
recombination between their non-sister chromatids.Meiosis | begin after
replication of parental chromosomes to form
identical sister chromatids at the S -phase.In
DIPLOID cell after Interphase the number of chromosomes remains the same( 2n)
BUT each chromosome change its shape
from single stranded (MONAD) to double
stranded(DYAD).In a DIPLOID cell the amount of DNA content changes from 2c to
Ac.Four haploid cells are formed at the end of the
Meiosis Il.
It is typically longer and more complex.
It includes 5- phases based on chromosomal
behaviour:Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
a. Leptotene (Leptonema):Chromatin
fibres become long slender chromosomes.Nucleus enlarges.
b. Zygotene (Zygonema):Chromosomes
become more condensed.Similar chromosomes start pairing together (synapsis)
with the help of a complex structure called synaptonemal complex.The paired
chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.Each pair of homologous
chromosomes is called a bivalent.
c. Pachytene (Pachynema):Comparatively
longer phase.Bivalent chromosome split into similar chromatids. This stage is
called tetrads. During this, recombination nodules
appear at which crossing over occurs. It leads to genetic recombination on homologous chromosomes.Crossing over: The
exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids of two homologous
chromosomes in the presence of an
enzyme, recombinase.Recombination is completed by
the end of the pachytene.
d. Diplotene (Diplonema):Dissolution
of the synaptonemal complex occurs.The recombined homologous chromosomes of the
bivalents
separates from each other except at the sites of
cross overs.These X shaped structures are called Chiasmata.
e. Diakinesis:Terminalisation
of chiasmata.
Chromosomes are fully condensed.The meiotic spindle
fibres originate from the poles to prepare the homologous chromosomes for
separation.Nucleolus and Nuclear envelope disappear.
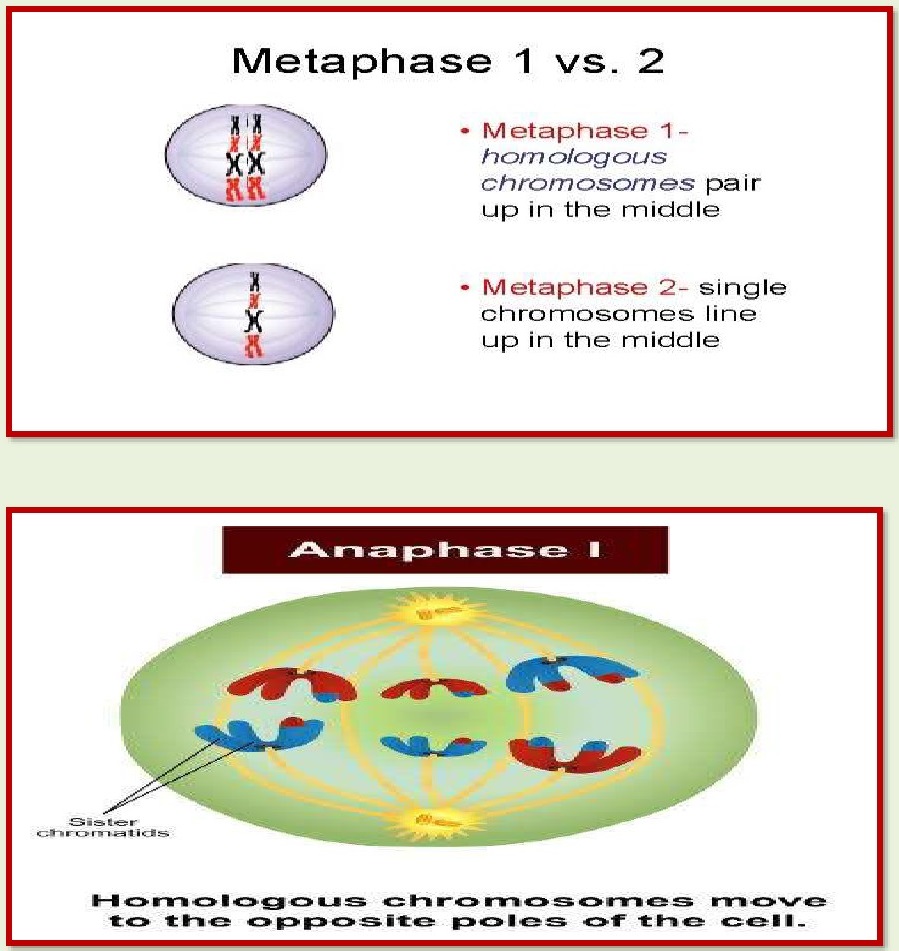
METAPHASE Spindle formation in completed.
The chromosomes align on the equatorial plate.The microtubules
from the spindle attach to the pair of : homologous chromosomes.
ANAPHASE
The
homologous chromosomes separate while sister chromatids
remain associated at their centromeres.
TELOPHASE The nuclear
membrane and nucleolus reappear.Two polar groups of DYAD chromosomes organise
themselves
into two daughter haploid nuclei with 2n amount of
DNA.Spindle fibres and astral rays disappear.After this, cytokinesis may or may
not occur.After a short interphase, it is followed by Meiosis Il.This short
stage between the two meiotic divisions is called interkinesis. DNA replication
does not occur in this phase.
SIGNIFICANCE OF MEIOSIS
It conserves the chromosome number of each species. It causes genetic variation
(due to crossing over) in the population of organism.
It is important for evolution.
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A) MCQs
1. Meiosis
results in:
a. Production of gametes
b. Introduction of variation
c. Reduction in chromosomes
d. All of the above
2. During
anaphase of meiosis:
a. Homologous chromosomes separate
b. Non-homologous autosomes separate
c. Sister chromatids separate
d. Non-sister chromatids separate
3.
Terminalisation is related to:
a. Meiosis |
b. Meiosis II
c. Meiosis
d. Cytokinesis
4. Bivalent are
arranged at the equator in:
a. Prophase-ll
b. Metaphase-ll
c. Metaphase-l
d. Anaphase-|
5. A bivalent of
meiosis-| consists of:
a. Two chromatids and one centromere
b. Two chromatids and two centromere
c. Four chromatids and two centromere
d. Four chromatids and four centromere
B) TRUE & FALSE:
1. Two cycles of DNA replication occurs in meiosis.
2. Chiasmata are observed in metaphase I.
3. Meiosis occurs in root tip.
C) FILL UPS
1. In meiosis haploid condition is reached by
........... stage.
2. Chiasmata are the expressions of ..............
PART A: VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS
A) MCQs
Ans. 1: d
It involves production of gametes, reduction in
chromosomes and introduction
of variation.
Ans. 2: a
Homologous chromosomes separates from centromere.
Ans. 3: a
Terminalisation is completed during diakinesis.
Ans. 4. ¢
Bivalent chromosomes align on the equatorial plate.
Ans. 5: ¢
Synapsis between homologous chromosomes leads to
formation of bivalent.
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. False: One cycle of DNA replication occurs before
meiosis 1 only.
2. True: A few Chiasmata are observed in metaphase
|.
3. False: Mitosis occurs in root tip. Meiosis occurs
only in germ cells to
form gametes.
C) FILL UPS
1. Anaphase - |
2. Crossing over
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Describe the following: i. Synapsis ii. Bivalent
iii. Chiasmata
2. What is crossing over? Give its significance.
3. What are homologous chromosomes? What happens to
homologous
chromosomes during meiosis?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is meiosis? Explain various stages of
prophase - | only.
A103
INTRODUCTION:MEIOSIS
It is the division of diploid germ cells that
reduces the chromosome
number by half forming haploid daughter cells
(gametes).It occurs during gametogenesis.It leads to the haploid phase in the
life cycle of sexually reproducing
organisms.Fertilisation restores diploid phase.
KEY FEATURES OF MEIOSIS:It
involves two cycles (meiosis | and meiosis Il) but only a single cycle of DNA
replication.It involves pairing of homologous chromosomes and recombination
between their non-sister chromatids.Meiosis | begins after replication of
parental chromosomes to form
identical sister chromatids at the S phase.
Four haploid cells are formed at the end of the
Meiosis II.
MEIOSIS Il It resembles the mitosis. It has the
following phases.
PROPHASE II:It is initiated
immediately after cytokinesis of meosis-1 The chromosomes again become compact.
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear in both
nuclei.
METAPHASE II:The
chromosomes align at the equator and the microtubules from
opposite poles of the spindle get attached to the
kinetochores of sister chromatids. Metaphasic plate is formed.
ANAPHASE II:It begins with
the simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each
chromosome which was holding sister chromatids
together.So the separated chromatids move towards opposite poles of the cell by
shortening of microtubules attached to kinetochores.
TELOPHASE II:The
two groups of chromosomes get enclosed by a nuclear envelope.
CYTOKINESIS follows resulting in the formation of
tetrads of cells,i.e., 4- haploid daughter cells.
SIGNIFICANCE OF MEIOSIS II:
Meiosis
-
Il is the second division of meiosis in which the replicated
chromosomes (in Meosis-1) split and single stranded
chromosomes (chromatids) pass on to daughter cells. So it maintains haploid
number of chromosomes obtained after Meiosis-l, changing 2n DNA content to 1n
DNA content of the cells. It is called HOMOTYPIC or EQUATIONAL division as it
maintains the same number of chromosomes.
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART A: VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) MCQs:
1. At which stage
of meiosis does the genetic constitution of gametes is
finally decided:
a. Metaphase — |
b. Anaphase - II
c. Metaphase - II
d. Anaphase - |
2. During which
stage of spermatogenesis the chromosomes are associated with tetrads?
a. Pachytene
b. Diplotene
c. Zygotene
d. Leptotene
3. Diploid
chromosome number is 8. What shall be the number of chromatids in each daughter
cell after meiosis- 1?
a. 8
b. 4
c. 2
d. 16
4. In eggs,
active period of growth and metabolism is:
a. Leptotene
b. Zygotene
c. Pachytene
d. Diplotene
5. Sister
chromatids separate and move to the opposite poles in:
a. Anaphase - II
b. Anaphase - |
c. Telophase -— ||
d. Telophase — |
B) TRUE / FALSE:
1. Meiosis involves two successive divisions,
resulting in 4 daughter cells.
2. Chiasmata are observed in metaphase - |.
3. Division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
C) FILL UPS:
1. Gi, S and G2 are sub phases of ............
2. Meiosis is best studied in smears of young
.............
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
A) MCQs:
Ans. 1: b
In this, splitting of centromere takes place.
Ans. 2: a
In this stage, bivalent chromosomes appear as
tetrads.
Ans. 3: a
Number remains same after meiosis.
Ans. 4: d
Diplotene can last for months or years. So, it is a
long stage.
Ans. 5: a
Splitting of centromere of each chromosome which
hold the sister chromatids.
B) TRUE & FALSE:
1. True
2. True
3. True
C) FILL UPS:
1. Interphase
2. Anthers
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Meiosis-Il is not mitosis. Why?
2. What is the significance of meiosis — II?
3. What is the need of meiosis — II?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Explain in detail meiosis — II.
A104
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A) MCQs
1. Mitosis is
characterised by:
a. Reduction division
b. both (a) and (b)
c. Equal division
d. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
2. In mitosis
centromere divides at
a. Metaphase
b. Anaphase
c. Telophase
d. Prophase
3. Main feature
of Anaphase of mitosis is:
a. Arrangement of chromosomes at equator
b. Spindle formation
c. Separation of daughter chromosomes
d. Cytokinesis
4. Chiasma
formation occurs in
a. Mitosis
b. Meiosis
c. Prophase
d. G2 phase
5. Meiosis occurs
in organisms during
a. Sexual reproduction
b. Asexual reproduction
c. Both a and b
d. None of these
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. Mitosis produces four daughter cells.
2. Mitosis occurs only in multicellular organisms.
3. Synapsis is present in meiosis.
C) EILL UPS
1. Somatic cells multiply by .
2. Mitosis produces no .
PART A: VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS
A) MCQs
Ans. 1:¢
EXPLANATION: in this division the chromosome remains
same in the daughter
cells.
Ans. 2:b
EXPLANATION: centromere divides and chromatids separate.
Ans. 3:¢
EXPLANATION: in this phase daughter chromosomes
separate
Ans. 4:b
EXPLANATION: in prophase-1 of meiosis chiasma
formation takes place.
Ans. 5: a
EXPLANATION: sexually reproducing organisms divides
by meiosis.
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. False
2. False
3. True
C) FILL UPS
1. Mitosis
2. Variations
1. Why is mitosis known as equational division?
2. What is the significance of meiosis?
1. Write down the difference between mitosis and
meiosis.
A105
INTRODUCTION:MITOSIS
1. It is the cell division occurring in somatic
cells.
2. It is also called as equational division as the
number of chrosomes in the parent and progeny cells is same.
3. The karyokinesis of mitosis has four stages:
Prophase,Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
1. PROPHASE
It is the longest phase in mitosis. It follows the S and G2 phases of
interface in the S and G2 phases, DNA molecules are intertwined.Chromosomal materials are untangled and condensed to form mitotic chromosomes. They are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere.
Chromosomes come to lie at the equator. The plane of
alignment of the chromosomes at the metaphase is called metaphase plate.
The spindle fibers from both poles are connected to
chromatids by their
kinetochores in the centromere.
Centromeres split and chromatids separate.Chromatids move to opposite poles.
Nuclear envelope develops around the chromosome clusters at each pole. So, two daughter nuclei are formed.The spindle fibers disappear.
It is the division of cytoplasm to form two daughter cells.It starts when telophase is in progress.
In plant cells, cytokinesis takes place by cell
plate formation.In animal cells, cytokinesis takes place by cell furrow.
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A) MCQs
1. Mitosis is
characterised by:
a. Reduction division
b. both (a) and (b)
c. Equal division
d. pairing of homologous chromosomes
2. In which stage
chromosomes arrange in the equatorial plate
a. prophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
d. none of these
3. In mitosis
centromere divides at
a. Metaphase
b. Anaphase
c. Telophase
d. Prophase
4. Which
statement is correct for anaphase
a. Chromatids move towards periphery.
b. Nuclear membrane appears.
c. Chromosomes become distinct.
d. None of these
5. Chromosome
number remains same in
a. S phase of cell cycle
b. Mitosis
c. G2 phase of cell cycle
d. Meiosis
B) TRUE & FALSE:
1. Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm.
2. Four daughter cells are produced in mitosis.
3. Chromatids move to opposite poles in anaphase.
C) FILL UPS:
1. Mitosis is division.
2.Karyokinesis is the division of .
A) MCQs
Ans. 1:¢
EXPLANATION:
In this division the chromosomes number remains same
in the daughter cells.
Ans. 2: b
EXPLANATION: chromosomes lie at equator plate in metaphase.
Ans. 3: b
EXPLANATION: In Anaphase stage centromere divides.
Ans. 4. a
EXPLANATION: Chromatids move towards periphery in
anaphase.
Ans. 5:6
EXLANATION: Because mitosis is equational division.
B) TRUE /FALSE:
1. True
2. False
3. True
C) FILL UPS:
1. equational
2. nucleus
1. Draw a labeled diagram of metaphase stage of
mitosis.
2. Identify following figures and name the stage.
1. Draw well labeled diagrams of mitosis.
A106
INTRODUCTION:MEIOSIS
-|
It is the division of diploid germ cells that
reduces the chromosome number by half, forming haploid daughter cells
(gametes).
It is divided into two parts that are KARYOKINESIS
and CYTOKINESIS.
KARY OKINESIS has four phases:
PROPHASE -I
It is typically longer and more complex.
It includes 5 phases based on chromosomal
behaviour:Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
a. LEPTOTENE (LEPTONEMA):Chromatin fibres
become long slender chromosomes.Nucleus enlarges.
b. ZYGOTENE (ZYGONEMA):Similar
chromosomes start pairing together (synapsis) with the help of a complex
structure called synaptonemal complex.Each pair of homologous chromosomes is
called a BIVALENT.
c. PACHYTENE (PACHYNEMA):Bivalent
chromosome split into similar chromatids.
Crossing over: The exchange of genetic material between
non sister chromatids of two homologous chromosomes in the
presence of an enzyme, recombinase.
d. DIPLOTENE (DIPLONEMA):Chiasma
formation takes place.
e. DIAKINESIS:Terminalisation
of chiasmata.
The meiotic spindle fibres originate from the
poles.Nucleolus and Nuclear envelope disappear.
METAPHASE -|Spindle
formation.The Bivalent chromosomes align on the equatorial plate.
ANAPHASE -
|The homologous chromosomes separate while sister chromatids remain associated
at their centromeres.
TELOPHASE -|The
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear and two haploid daughter nuclei are
formed.After this, cytokinesis may or may not occur.
Dear students,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A) MCQs
1. Meiosis
results in:
a. Production of gametes
b. Introduction of variation
c. Reduction in chromosomes
d. All of the above
2. During
anaphase — | of meiosis:
a. Homologous chromosomes separate
b. Non-homologous autosomes separate
c. Sister chromatids separate
d. Non-sister chromatids separate
3.
Terminalisation is related to:
a. Meiosis |
b. Meiosis II
c. Meiosis
d. Cytokinesis
4. Bivalent are
arranged at the equator in:
a. Prophase-ll
b. Metaphase-ll
c. Metaphase-l
d. Anaphase-|
5. A bivalent of
meiosis-| consists of:
a. Two chromatids and one centromere
b. Two chromatids and two centromere
c. Four chromatids and two centromere
d. Four chromatids and four centromere
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. Bivalent is formed during zygotene stage.
2. Chiasmata are observed in metaphase I.
3. Meiosis occurs in germ cells.
C) FILL UPS
1. In meiosis haploid condition is reached by
..............stage.
2. Chiasmata are the expressions of ..............
A) MCQs
Ans. 1: d
EXPLANATION: It involves production of gametes,
reduction in chromosomes and introduction of variation.
Ans. 2: a
EXPLANATION: Homologous chromosomes separate from
centromere.
Ans. 3:a
EXPLANATION: Terminalisation is completed during
diakinesis of Prophase-1
of Meiosis -1.
Ans. 4: ¢
EXPLANATION: Bivalent chromosomes align on the
equatorial plate.
Ans. 5:¢
EXLANATION: Synapsis between homologous chromosomes
leads to formation of bivalent.
B) TRUE & FALSE
1. True
2. False: Chiasmata are observed in Diplotene of
prophase - I.
3. True
C) FILL UPS
1. Anaphase - |
2. Crossing over
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Draw diagram of prophase-1.
2. Draw diagram where Chiasmata is formed.
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is meiosis? Draw diagrams of meiosis-2 only.
A107
INTRODUCTION:CELL
DIVISION is a process in which parent cell after replication of its component
s,divides to form new (daughter) cells. A cell divides by two methods: MITOSIS
and MEIOSIS.In this cell division daughter cells have equal number of
chromosomes and amount of DNA as that of the parent. Itis known as [A or ED |t
occurs in somatic cells.
1. Daughter cells are identical to the parents as
itis an equational cell division having equal number of chromosomes and same
amount of DNA as the parent.
2. Restores the proper size of the cell.
3. Related to the growth of an individual as occurs by
increasing the number of cells.
4. Helps in vegetative propagation and asexual
reproduction of organisms.
5. In unicellular organisms lead to asexual
reproduction.
6. Responsible for healing wounds, repairing cells
and regeneration of body cells.
7. Occurs in somatic cells and leads to somatic
variations.
8. Maintains haploid and diploid genetic
constitution.
It is reductional cell division as chromosomes are
reduced from diploid to haploid ,occurs in germ cells of gonads (testis/ovary)
during the formation of gametes.
1. Essential in the life cycle of all the sexually
reproducing organisms.
2. Helps in maintaining the same number of
chromosomes in a species.
3. Responsible for variations and evolution as it
develops new varieties and brings
about gene mutations.
4. Similar in all the sexually reproducing organisms
which shows their basic similar
evolutionary relationship.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) Multiple choice questions:
1. Mitosis is characterized
by :
(a) Reduction division
(b) Equational division
(c) Both reduction and equational
(d) None
2. Meiosis occurs
in organisms during:
(a) Sexual reproduction
(b) Vegetative reproduction
(c) Both sexual and vegetative reproduction
(d) None
3. Meiosis
results in:
(a) Production of gametes
(b) Introduction of variations
(c) Reduction in the number of chromosomes
(d) all of the above
4. A somatic cell
divides by:
(a) Mitosis
(b) Meiosis
(c) Both mitosis and meiosis
(d) Vegetative propagation
5. Identify the
wrong statement about meiosis:
(a)Occurs in sexually reproducing organisms
(b)Reduction in the chromosome numbers to half
(c)Responsible for gene mutations
(d)Occurs in somatic cell
B) Fill in the blanks:
1. Somatic cells multiply by ;
2. Mitosis results in the formation of nucleus
having number of chromosomes.
3. Mitosis helps in vegetative reproduction and
reproduction.
C) True/False:
1. Meiosis is responsible for the development of new
varieties.
2. Meiosis is an equational division.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
A)Multiple choice questions:
1. (b) In mitosis daughter cells have equal number
of chromosomes and amount
of DNA as that of parent cell.
2. (a) Meiosis occurs in sexually reproducing
organisms.
3. (d)Meiosis leads to variations, number of
chromosomes are reduced to half,
occurs in gonads.
4. (a) Asomatic cell divides by mitosis.
5. (d)Meiosis occurs in germ cells inside gonads..
B) Fill in the blanks:
1. Mitosis It occurs in somatic cells
2. Same Daughter cells formed during mitosis have
same no. of chromosomes
and amount of DNA as that of parent cell.
3. Asexual.
C) True/False:
1. True
2. False: Meiosis is a reductional division.
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Why is mitosis known as equational division?
2. Define meiosis.
3. What is cell division?
PART: C_ LONG
ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is the significance of Mitosis and Meiosis?
A108
RECAPITULATION:CELL DIVISION is a process in which parent cell after replication of its components,divides to form new (daughter) cells. A cell divides by two methods: MITOSIS and MEIOSIS.In this cell division daughter cells have equal number of chromosomes and amount of DNA as that of the parent. It is known as i or . |t occurs in somatic cells.
It is reductional cell division as chromosomes are
reduced from diploid to haploid,occurs in germ cells of gonads (testis/ovary)
during the formation of gametes.
NOW LET US DO NCERT QUESTIONS ANSWERS:
Question 1:What
is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Answer 1:The average cell cycle span for a mammalian
cell is approximately 24 hours.
Question
3:Describe the events taking place during interphase.
Answer 3:Interphase involves a series of changes
that prepare a cell for division. It is a period during which the cell
experience growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner.Interphase is
divided into three phases.G: phase S phase
G2 phase
G, phase - It is the stage during which the cell
grows and prepares its DNA for
replication. In this phase, the cell is
metabolically active.S phase (Synthesis) — During this stage, the synthesis of
DNA takes place. The DNA quantity doubles whereas the number of chromosomes
remains unchanged.G2 phase (Gap 2) — During this phase, the cell advances to
grow and prepare itself for division. It is during this stage that the RNA and
proteins that are required for mitosis are generated.
Question4:What
is Go (quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Answer 4:In adult animals some cells will not
exhibit the cell division, and many other cells occasionally divide when there
is need to replace cells that have lost because of injury or cell death. These
cells exit the G; phase to enter inactive stage of the cell cycle called Gp
phase. Cells in Go phase do not proliferate unless called on to do so.Hence,
the cells in this phase tend to become inactive, stop dividing and become
specialized through the differentiation process.
Question5:Why
mitosis is called equational division?
Answer 5:Mitosis is called equational division
because the number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same.
Question 6:Name
the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur:
(i) Chromosomes
are moved to spindle equator.
(ii) Centromere
splits and chromatids separate.
(iii) Pairing
between homologous chromosomes takes place.
(iv) Crossing
over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Answer :6 i) Chromosomes are moved to the spindle
equator in the Metaphase.
ii) Centrosomes split and chromatids separate in the
Anaphase.
iii) Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes
place in the Zygotene stage of
prophase-1 in meiosis.
iv) Crossing over between homologous chromosomes
takes place during the
Pachytene stage of prophase -1 in meiosis.
Question
7:Describe the following:
(a) synapsis
(b) bivalent
(c) chiasmata
Draw a diagram to
illustrate your answer.
Answer :7 a) SYNAPSIS — Homologous
chromosomes pair together during Zygotene of prophase-| of meiosis. This
pairing is called synapsis.
b) BIVALENT or TETRAD
is the pair of complex formed by a pair of synapsed
homologous chromosome during the zygotene of
prophase | of meiosis.
c) CHIASMATA
-During DIPLOTENE, the paired chromosomes form an X-shaped structure known as
chiasmata. At chiasmata, the crossing over between two non-
sister chromatids takes place.
Question :9 Find
examples where the four daughter cells from meiosis are equal in size and where
they are found unequal in size.
Answer :9During formation of male gametes in human
beings (sperms), four daughter cell formed during meiosis are equal in size.
The formation of female gamete (ovum)
during meiosis results in formation of four daughter
cells, unequal in size. The
unequal daughter cells are — one big mature ovum and
3 small polar bodies.
Question :12 What
is the significance of meiosis?
Answer :12 Significances of Meiosis:
It conserves specific chromosome number of each
species achieved across
generations.Enhances the genetic variability in the
population of organisms from generation to generation. These variations are
significant for the evolution process.It produces gametes for sexual
reproduction Promotes crossing over. It introduces a new combination of
variations or traitsChromosomal mutations can occur due to abnormalities during
meiosis. a few of these can be beneficial to organisms.
Question :13 Discuss with your teacher about
(i) haploid
insects and lower plants where cell-division occurs.
(ii) some haploid
cells in higher plants where cell-division does not occur.
Answer :13
i) Haploid insects where cell division occurs is
drones of honey bee and lower plants are Spirogyra, Chlamydomonous,
Pteridophytes. These haploid gametes are
produced by them through mitosis and not meiosis.
ii) Spermatozoa and ova of higher animals and
microspores of higher plants will not
undergo cell division.
Question :14 Can
there be mitosis without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase?
Answer :10 During S - phase, DNA synthesis or
replication of DNA takes place. DNA replication is essential for cell division.
Without DNA replication, cell division will not take
place.
Question :15 Can
there be DNA replication without cell division?
Answer :15 Yes, DNA replication can take place
without cell division. In order to prepare for cell division, DNA replication
is necessary. Cell division is the succeeding logical step that occurs post
cell division.
Question :16Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and notice how the
following two parameters change:
(i) Number of chromosomes (N) per cell
(ii) Amount of DNA content (C) per cell
Answer :16
i) DNA replication can take place in G; phase of
cell cycle. The number of
chromosomes remains the same and each chromosome is
formed from one
chromatid. In the S phase, chromosome is formed by
two sister chromatids joined at
the centromere. Similar conditions continue in the
G2 phase, while in M phase, sister
chromatids separate and move to different cells. The
number of chromosomes stays
the same in mitosis.
ii) Amount of DNA content in the cell remains the
same in G: phase but in S phase it doubles as the DNA replication takes place.
It remains double in G2 phase but
halved in the M phase of the cell cycle.
A109
INTRODUCTION:CELL
DIVISION is a process in which parent cell after replication of its
components,divides to form new (daughter) cells. A cell divides by two methods:
MITOSIS and MEIOSIS.Dear students we have completed the last chapterno.10, in
unit no.3 We have done all the possible different types of questions including
NCERT exercise questions in the previous assignments.In this assignment we will
revise all the diagrams included in this chapter.
A110
RECAPITULATION:Cell
cycle: the sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome,synthesizes
other constituents of the cell and divides into two daughter cells.Phases of
cell cycle:SeG: phase: cell metabolically becomes active and grows
continuously.S phase: synthesis of DNA but number of chromosomes remains same.
G» phase:
synthesis of proteins while cell continues to grow.Rn © starts with nuclear
division, separation of daughter
chromosomes (karyokinesis) ends with cytokinesis
(division of cytoplasm)
EE nactive stage, cells do not differentiate but
remain active Cell division is a part of cell cycle and occurs in dividing
cells. A cell can divide
by two methods: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis:
Equational (somatic) cell division, daughter cells have equal number
of chromosomes and equal amount of DNA as that of
parent cell. Occurs in somatic cell. Flemming coined the term mitosis
Mechanism of mitosis: Two steps:
Karyokinesis -1 : Division of nucleus into nuclei .
(a) Prophase
: It is of longest duration , chromatin threads appear ,chromosomes duplicate ,
chromatids are formed ,nucleus disappears nuclear membrane starts
disintegrating nuclear membrane disappears
, spindle fibres are formed.
(b) Metaphase:
Chromosomes arrange themselves around the equator of the spindle (congression).
(c) Anaphase =~:
Centromere divides into two , chromatids of each chromosome move apart towards
opposite poles of the spindle.
(d) Telophase : Chromatids are organized
into chromatin material nuclear membrane is formed , nucleolus appears, 2-
daughter nuclei are formed having same number and shape of chromosomes as
parent nucleus .
Cytokinesis : division of cytoplasm after karyokinesis
Significance of mitosis : maintenance
of chromosome number , growth or addition of cells ,regeneration , reproduction
in unicellular organisms, repair and wound healing.
Meiosis :;
Reduction of chromosomes from diploid to haploid conditions,occurs in germ
cells of gonads (testis/ovary) during the formation of gametes
Mechanism of meiosis
: Two meiotic divisions:
Meiosis 1:
It is reductional division
Karyokinesis1 (a) Prophase 1 : long duration, has 5
substages:Leptotene =: nucleus increases in size , centrospheres becomes indistinct
, centrioles separate , astral rays appear
Zygotene
: pairing(synapsis) of homologous chromosomes (bivalent) ,nucleolus is distinct
Pachytene : chromosomes
shorten and thicken, become indistinct ,tetrads appear , crossing over occurs,
nucleolus still distinct , two asters move apart .
Diplotene:
synaptonemal complex dissolves.
Diakinesis :
bivalents separate , move towards the periphery of the nucleus , nucleolus
disappears
(b) Metaphase 1
: bivalents get arranged at equator for equal distribution of
chromosomes , chromosomes replicate
(c) Anaphase 1:
homologous chromosomes separate , dyads are formed.
(d) Telophase 1
: dyad chromosomes organize into two daughter haploid ,formation of nuclei ,
nucleoli , nucleoplasm , nuclear envelope
Cytokinesis : division of
cytoplasm which occurs through cleavage, produces
2 daughter cells with nuclei having haploid number
of dyad chromosomes .
Interkinesis :
brief phase between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
Meiosis 2
1. Karyokinesis 2:
(a) Prophase 2 : chromosomes shorten , divergent
chromatids , nucleolus
disappears
(b) Metaphase 2_:
spindle apparatus appears , chromosomes connect to spindle fibres which bring
chromosomes in the equator of the spindle. At the end each poles has haploid
no. of chromosomes .
(c)Anaphase 2: centromere of
each chromosome splits allowing them to
move towards opposite poles of the cell . chromatids
separate
(d) Telophase 2
: Each polar group forms nucleus. Astral rays and spindle
fibres disappears
2. Cytokinesis
: occurs by cleavage
Significance of meiosis Formation of gametes in
sexually reproducing organisms
Genetic variability Maintenance of chromosomal
number
PART: A- VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) Multiple choice questions
1. Meiosis in
diploid organisms results in:
(a) Production of gametes
(b) reduction in the number of chromosomes
(c) Introduction of variation
(d) all of the above
2. At which stage
of meiosis does the constitution of gametes is finally
decided:
(a) Metaphase - 1
(b) Anaphase - 2
(c) Metaphase -2
(d) Anaphase - 1
3. Meiosis occurs
in organisms during:
(a) Sexual reproduction
(b) vegetative reproduction
(c) Both sexual and vegetative propagation (d) none
of the above
4. During
anaphase 1 of meiosis:
(a) homologous chromosomes separate
(b) non homologous autosomes separate
(c) sister chromatids separate
(d) non-sister chromatids separate
5. Mitosis is not
characterized by:
(a) Reduction division
(b) Equal Division
(c) Both reduction and equal division
(d) none of the above
6. Identify the
wrong statement about meiosis:
(a) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
(b) Four haploid cells are formed
(c) Appearance of chromosomes with two chromatids
joined together at
the centromere.
(d) Two cycles of DNA replication occur
B) Fillin the blanks
7. During sds stage chromosomes are arranged in
equatorial plate.
8. During meiosis chromatids of individual
chromosomes separate in stage.
9. dissolves during diplotene stage of prophase -1
of meiosis.
C) True /False
10. Gois the inactive stage of cell cycle
11. Crossing over occurs between non - sister
chromatids of a bivalent.
ANSWER KEY: (PART- A)
A) Mulitiple choice questions:
1. (d). in meiosis chromosomes are reduced to half ,
occurs in sexually reproducing organisms.
2.(d). during anaphase 1 two groups of dyad
chromosomes are formed having half the number of chromosomes present in the
mother cell
3. (a). Meiosis occurs in sexually reproducing
organisms
4. (a). In anaphase 1 homologous chromosomes
separate
5. (d). Mitosis is an equational division in which
the number of chromosomes is equal in both the daughter cells.
6. (d). In meiosis pairing of homologous chromosomes
occur, four haploid cells are formed
B)Fill in the blanks:
1. Metaphase. During this ,chromosomes arrange
themselves at the
equator
2. Anaphase. Chromatids separate and start moving
apart from each other
3. Synaptonemal complex dissolves except at
chiasmata during diplotene.
C) True /False:
1. True. Go is the inactive stage of cell division
in which cell does not
differentiate
2. True. Crossing over occurs between noon sister-
chromatids
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Distinguish between anaphase of mitosis and
anaphase -1 of meiosis.
2. Write the significance of meiosis.
3. Why is mitosis called equational division?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Describe the events occurring during interphase.
2. Describe the following. Draw diagrams to
illustrate the answer.
a) Synapsis
b)bivalent
c) Chiasmata.